- :::Home
- HK Technologies
- Xeno-free BDACs
Xeno-free BDACs
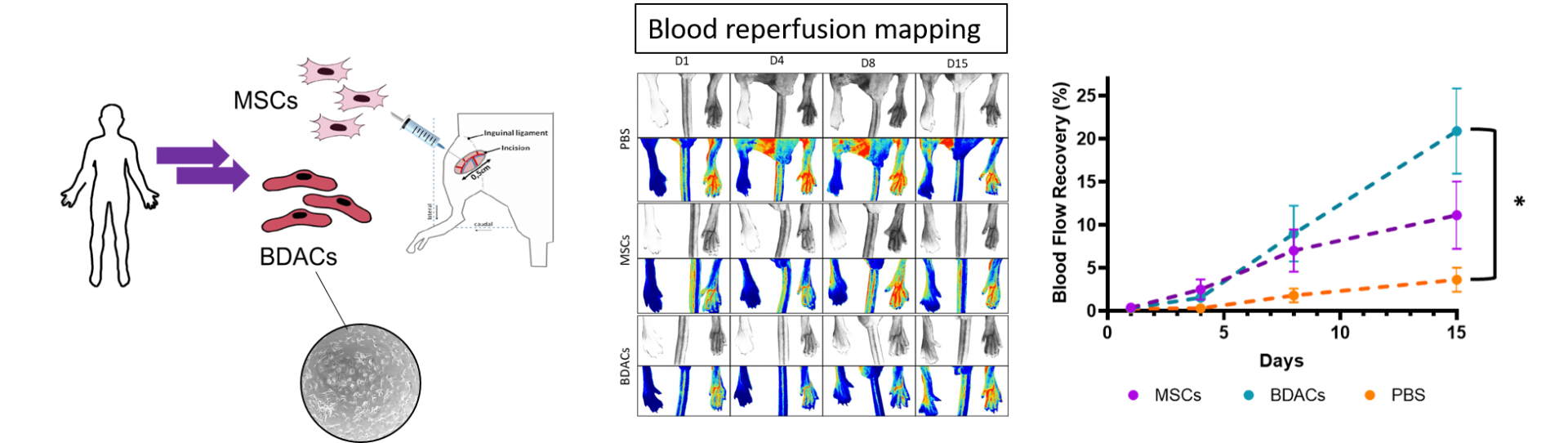
Establishment of a procedure to isolate and culture human peripheral blood-derived angiogenic cells (BDACs) for the treatment of ischemic diseases and comparing their therpaeutic efficacy for the treatment of Critical limb ischemia (CLI) to the current godl-standard (Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)).
CLI is the most severe form of peripheral artery disease with impaired blood supply to peripheral tissues and results in hypoxia, inflammation, vascular dysfunction and muscle degeneration. Patients with CLI experience rest-pain, non-healing ulcers, gangrene and are at high risk of lower extremity amputations. Hence, CLI is a major cause of disability and a major socio-economic burden globally.
- Isolation of BDACs under xeno-free (animal component free culture) conditions - paving the way their clinical application
- Sourcing BDACs in clinically relevant numbers and time frame
- Demonstrating its superior therapeutic potential as compared to the current therapeutic gold standard, MSCs
- The patient's own cells can be isolated from an easily accesible source (periheral blood) and utilized without major risks or discomfort for the patient.
- Cells can be sourced under GMP-compliable conditions
- BDACs performed better than the current gold-standard, MSCs.
- Results were presented at: Joint Meeting of ESCHM-ISCH-ISB 2021
- Results will be presented at TERMIS-AP 2022
- Manuscript with the most recent data is currently under revision in SCRT.
- Cell-based therapy for the treatment of CLI
Founded in 1963, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) is a forward-looking comprehensive research university with a global vision and a mission to combine tradition with modernity, and to bring together China and the West. CUHK teachers and students hail from all around the world. Four Nobel laureates are associated with the university, and it is the only tertiary institution in Hong Kong with recipients of the Nobel Prize, Turing Award, Fields Medal and Veblen Prize sitting as faculty in residence. CUHK graduates are connected worldwide through an extensive alumni network. CUHK undertakes a wide range of research programmes in many subject areas, and strives to provide scope for all academic staff to undertake consultancy and collaborative projects with industry.

-
 Anti COVID-19 Stainless Steel
Anti COVID-19 Stainless Steel -
 Therapeutic Inhibitor for Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-associated Cancers
Therapeutic Inhibitor for Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-associated Cancers -
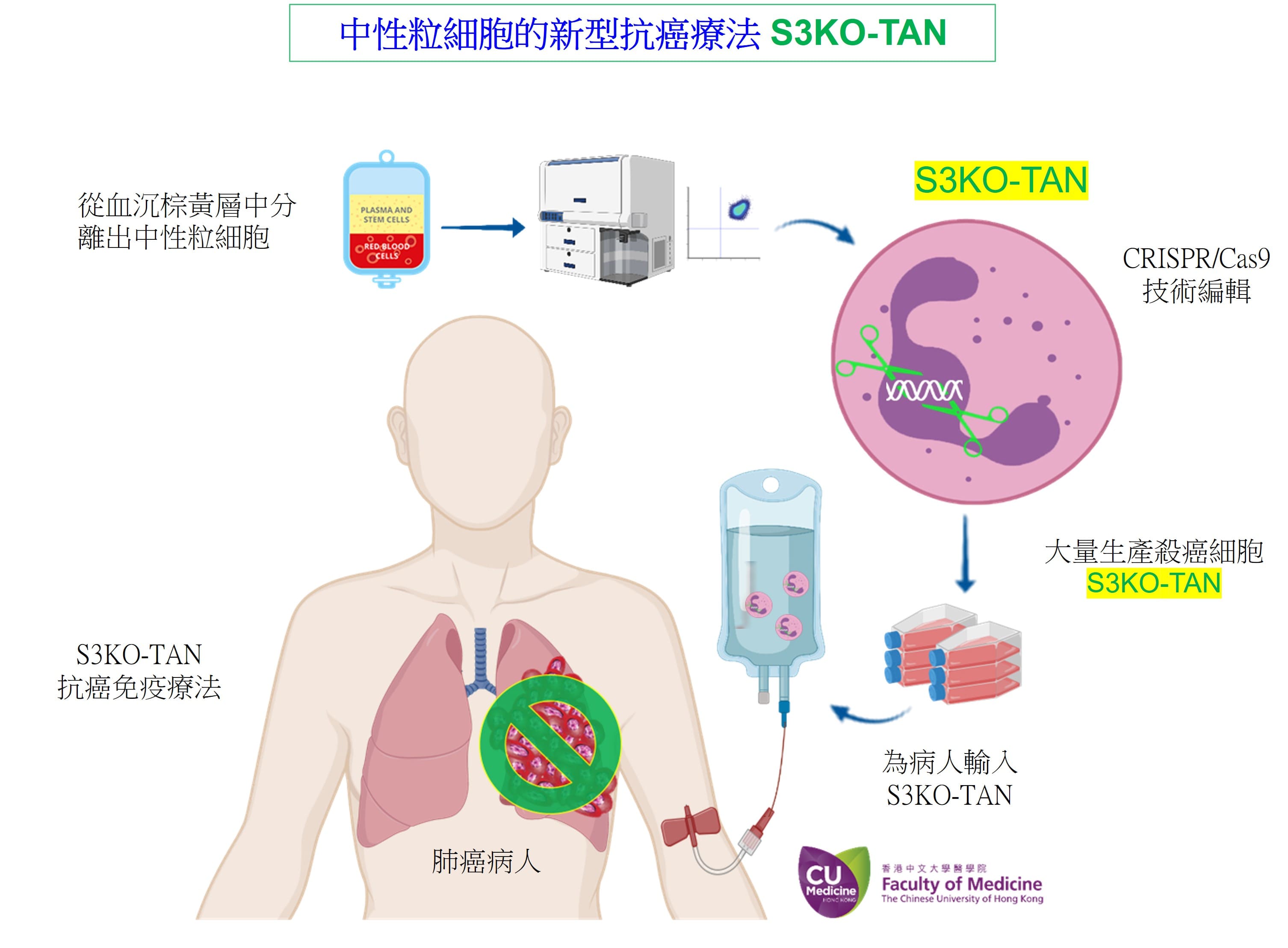 A Novel Neutrophil Anticancer Immunotherapy S3KO-TAN
A Novel Neutrophil Anticancer Immunotherapy S3KO-TAN -
 Copper-based Air Filter with Fast Virus Inactivation Ability
Copper-based Air Filter with Fast Virus Inactivation Ability -
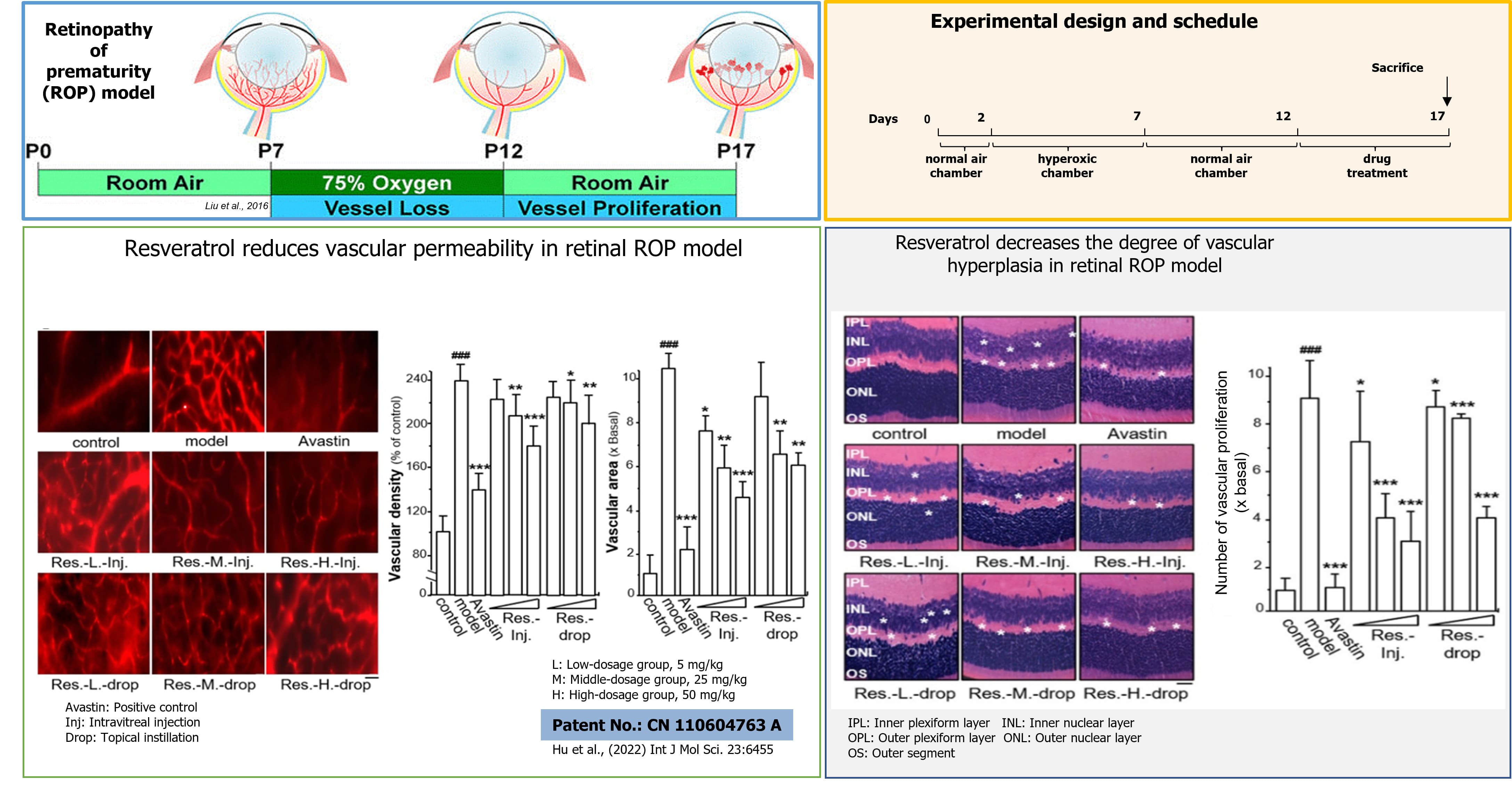 Optic Therapeutics Against age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Optic Therapeutics Against age-related macular degeneration (AMD) -
 Wearable AI Device for Elderly Fall Risk Assessment
Wearable AI Device for Elderly Fall Risk Assessment -
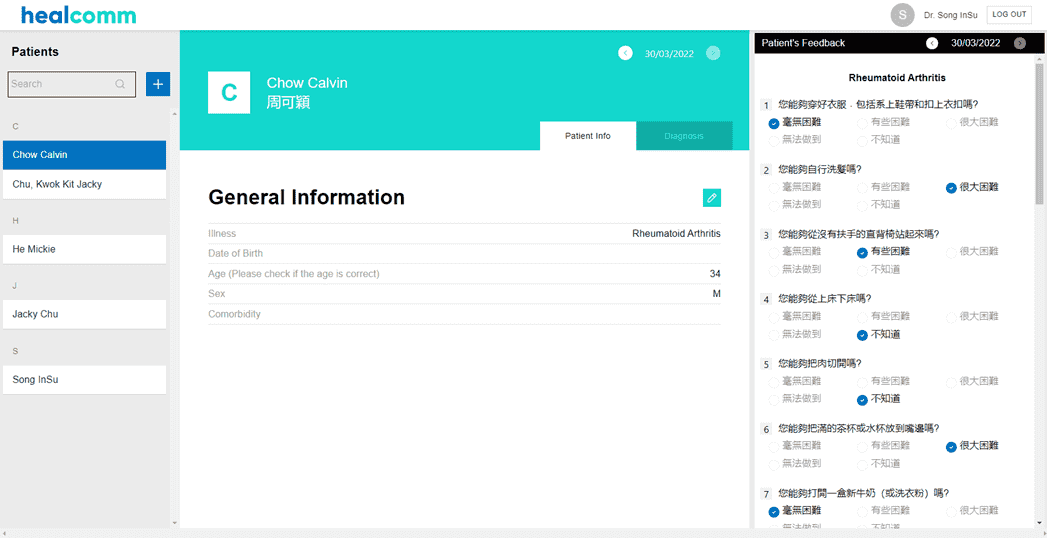 Next Generation End-to-End Healthcare Community Support System
Next Generation End-to-End Healthcare Community Support System -
 A software for automated compressive vertebral fracture detection on elderly women’s lateral chest radiograph: Ofeye 1.0
A software for automated compressive vertebral fracture detection on elderly women’s lateral chest radiograph: Ofeye 1.0 -
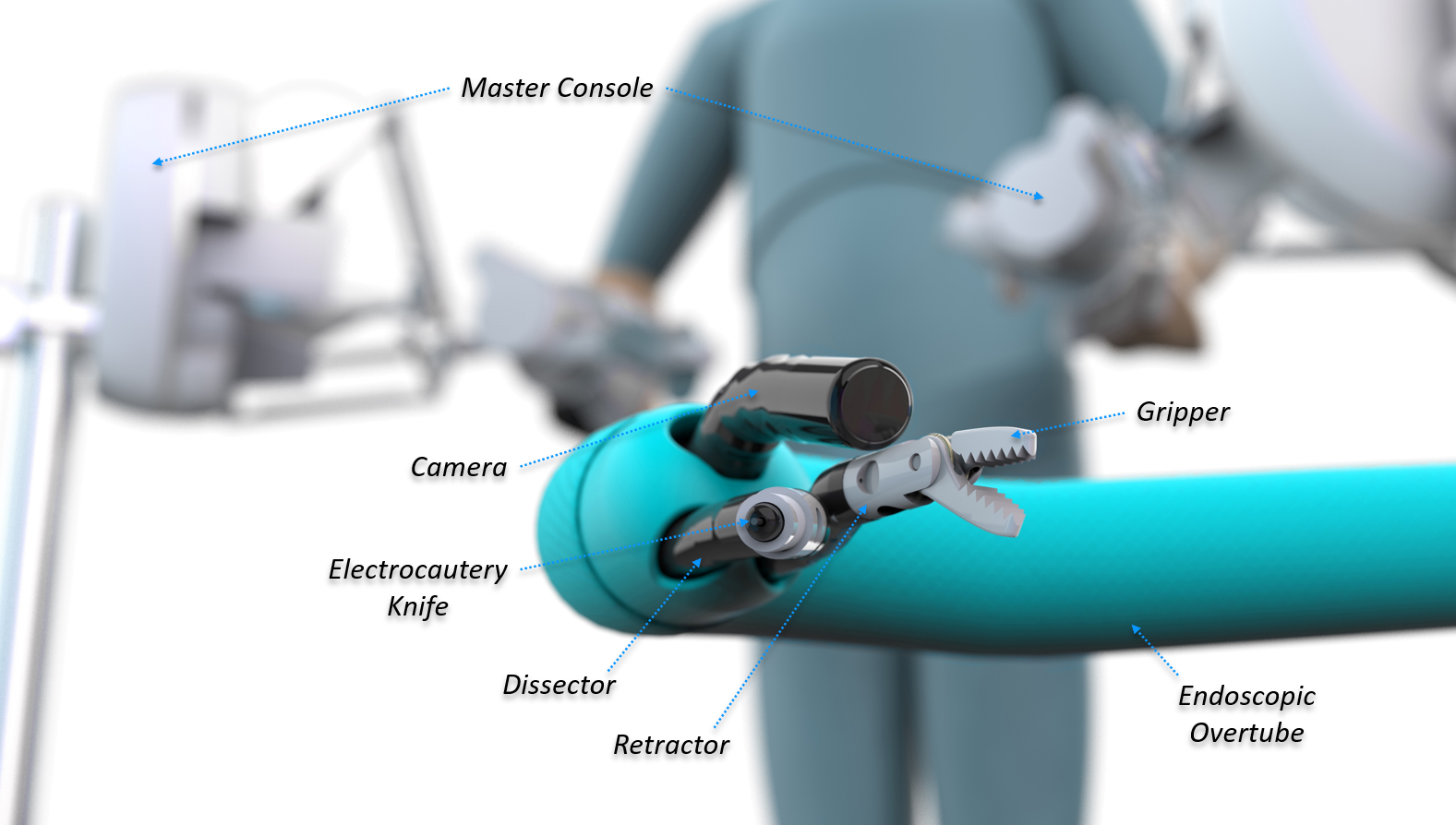
Robotic Endoscopic Platform for Performance of Advanced Endoluminal Surgery
-
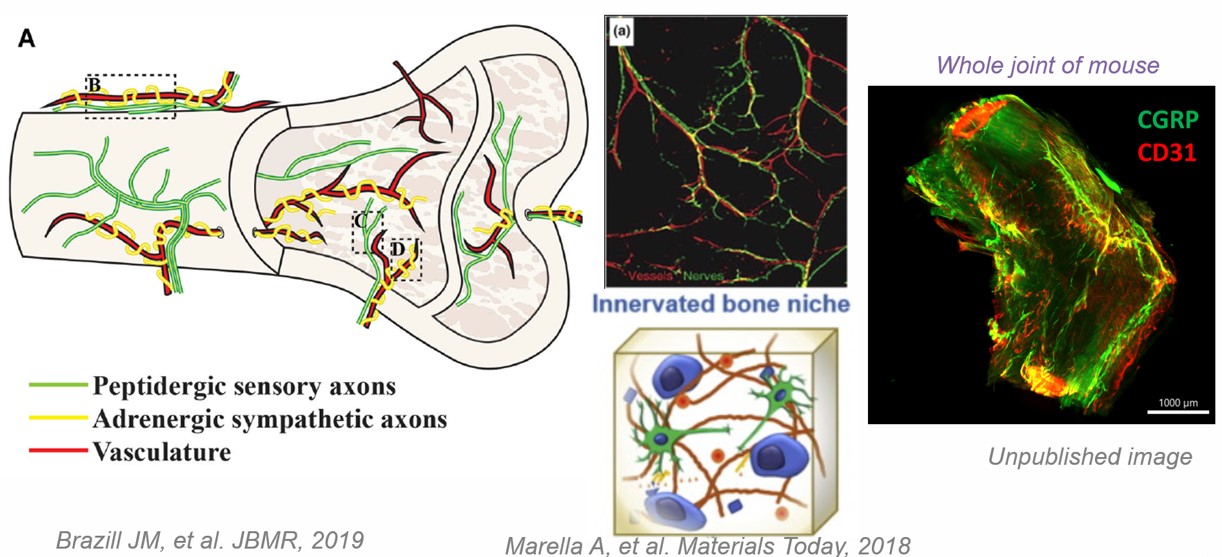 Bio-products for recapitulating nerve-vessel-bone network
Bio-products for recapitulating nerve-vessel-bone network -
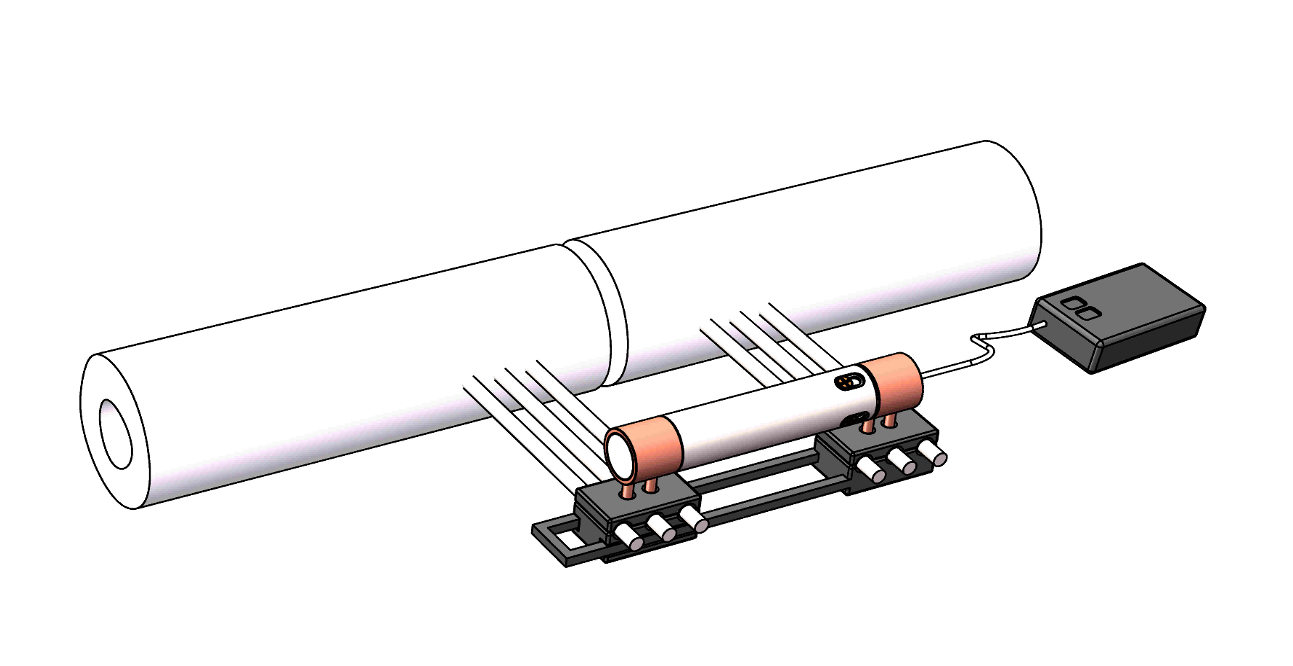 Universal Fracture Healing Accelerator for External Fixators
Universal Fracture Healing Accelerator for External Fixators -
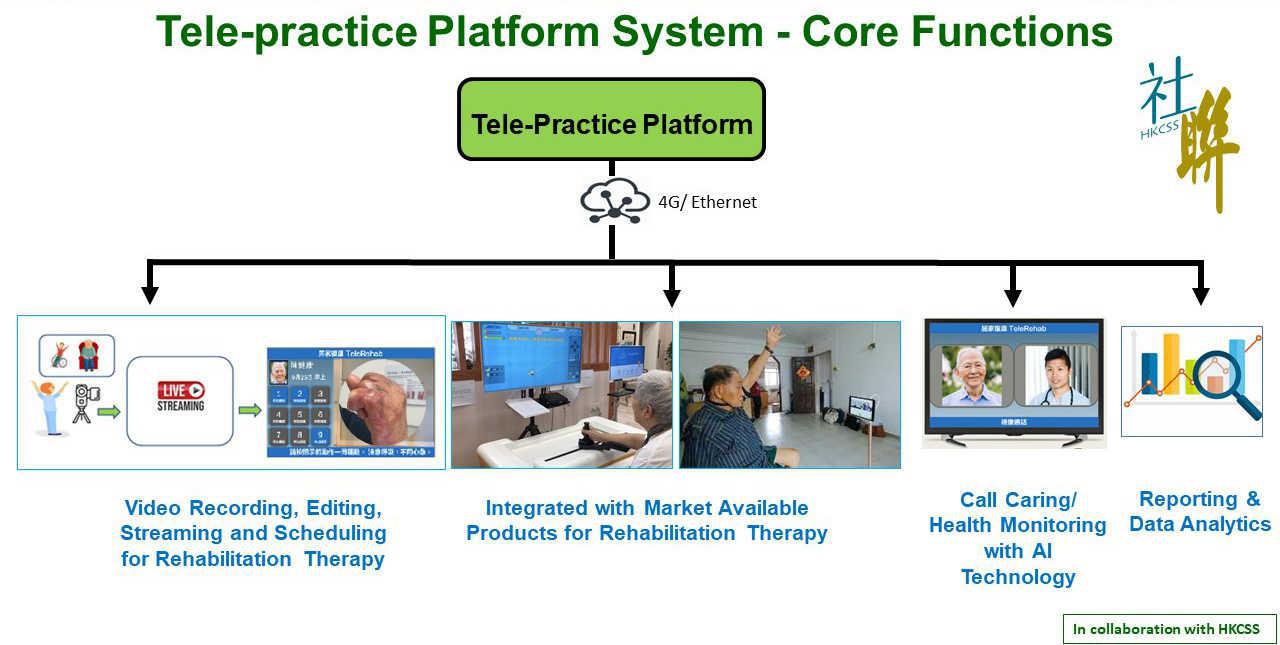 Tele-practice Platform System
Tele-practice Platform System -
 Magnetically-guided Endoscope (MGE) for Complete Small Bowel Examination and Diagnosis and Treatment of Small Bowel Diseases
Magnetically-guided Endoscope (MGE) for Complete Small Bowel Examination and Diagnosis and Treatment of Small Bowel Diseases -
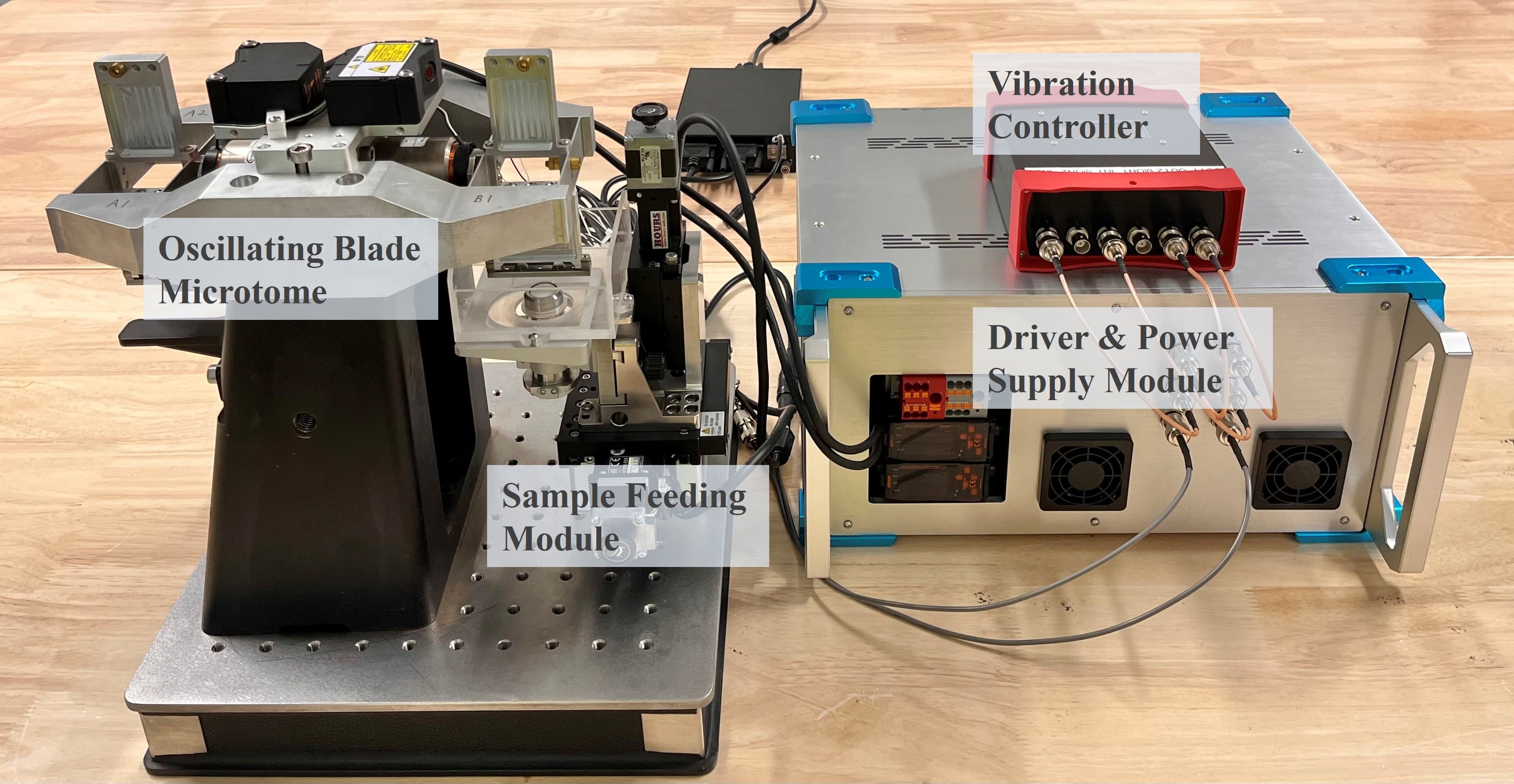 Ultrafast oscillating blade microtome
Ultrafast oscillating blade microtome -
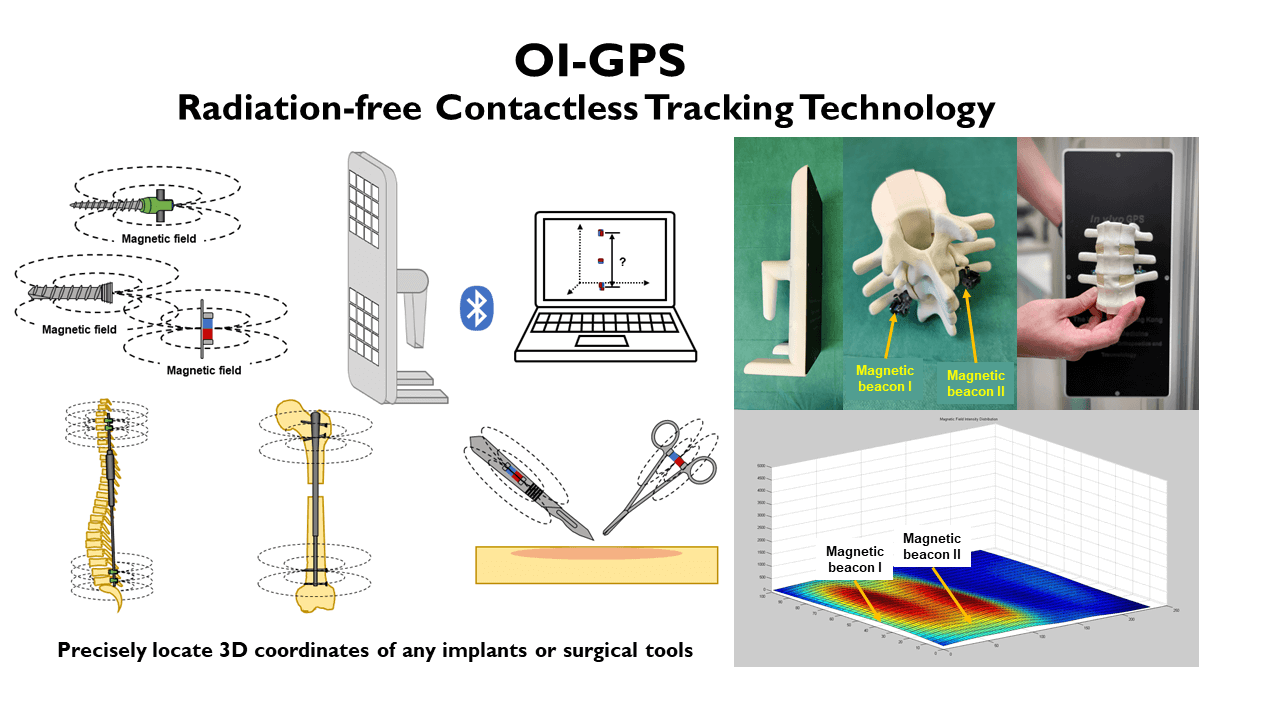 Non-contact, non-radiation device that accurately locates multiple body implants
Non-contact, non-radiation device that accurately locates multiple body implants -
 Aptamer-based Technology for Medical Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications
Aptamer-based Technology for Medical Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications -
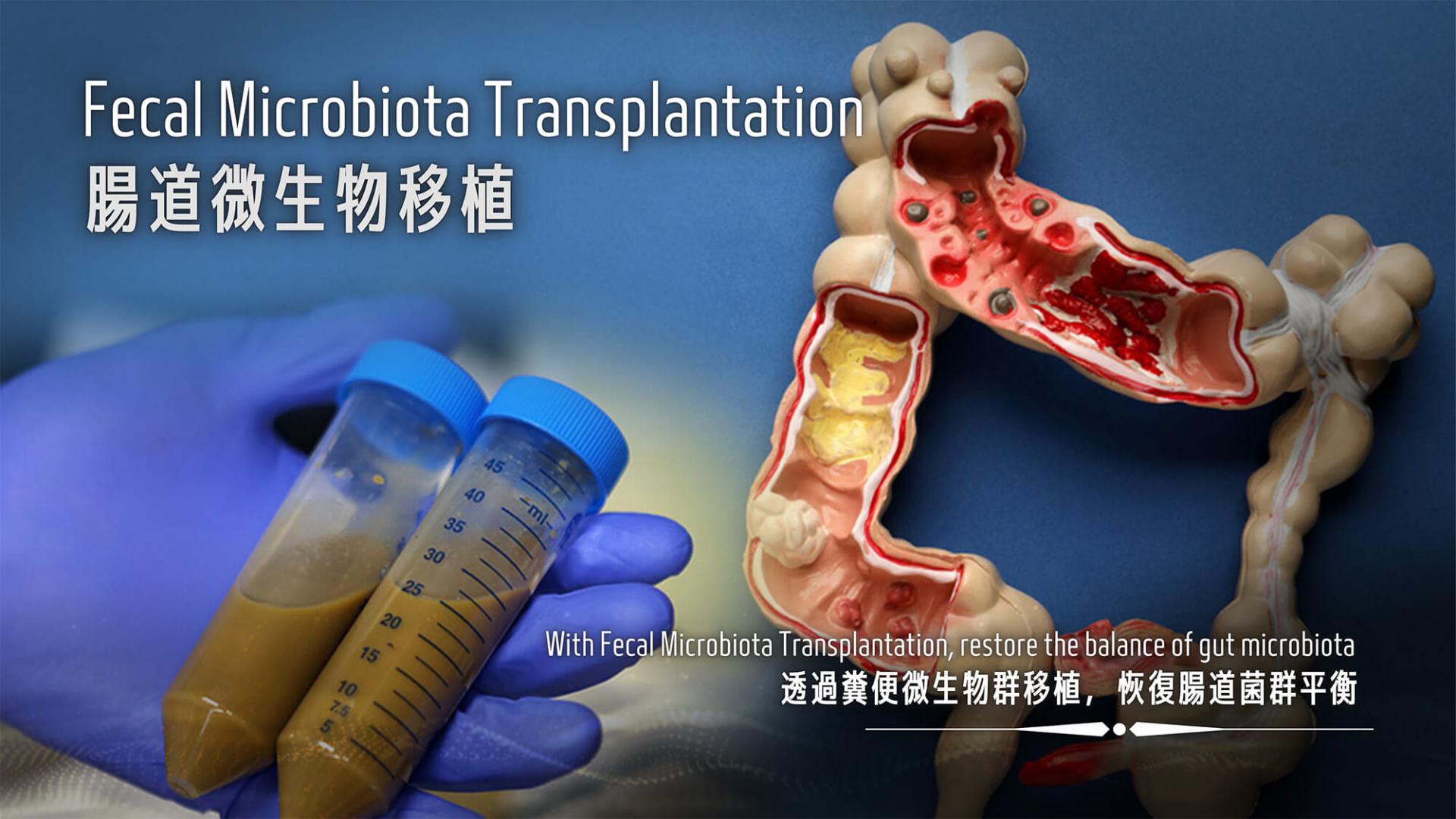 Artificial Intelligence-guided and Personalised Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) Treatment for Human Diseases
Artificial Intelligence-guided and Personalised Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) Treatment for Human Diseases -
 An Innovative Spinning System for Chitosan Yarn
An Innovative Spinning System for Chitosan Yarn -
 “StayHomeSafe” Home Quarantine Support Solution
“StayHomeSafe” Home Quarantine Support Solution -
 Synthetic patentiflorin A analogs as antiviral agents
Synthetic patentiflorin A analogs as antiviral agents -
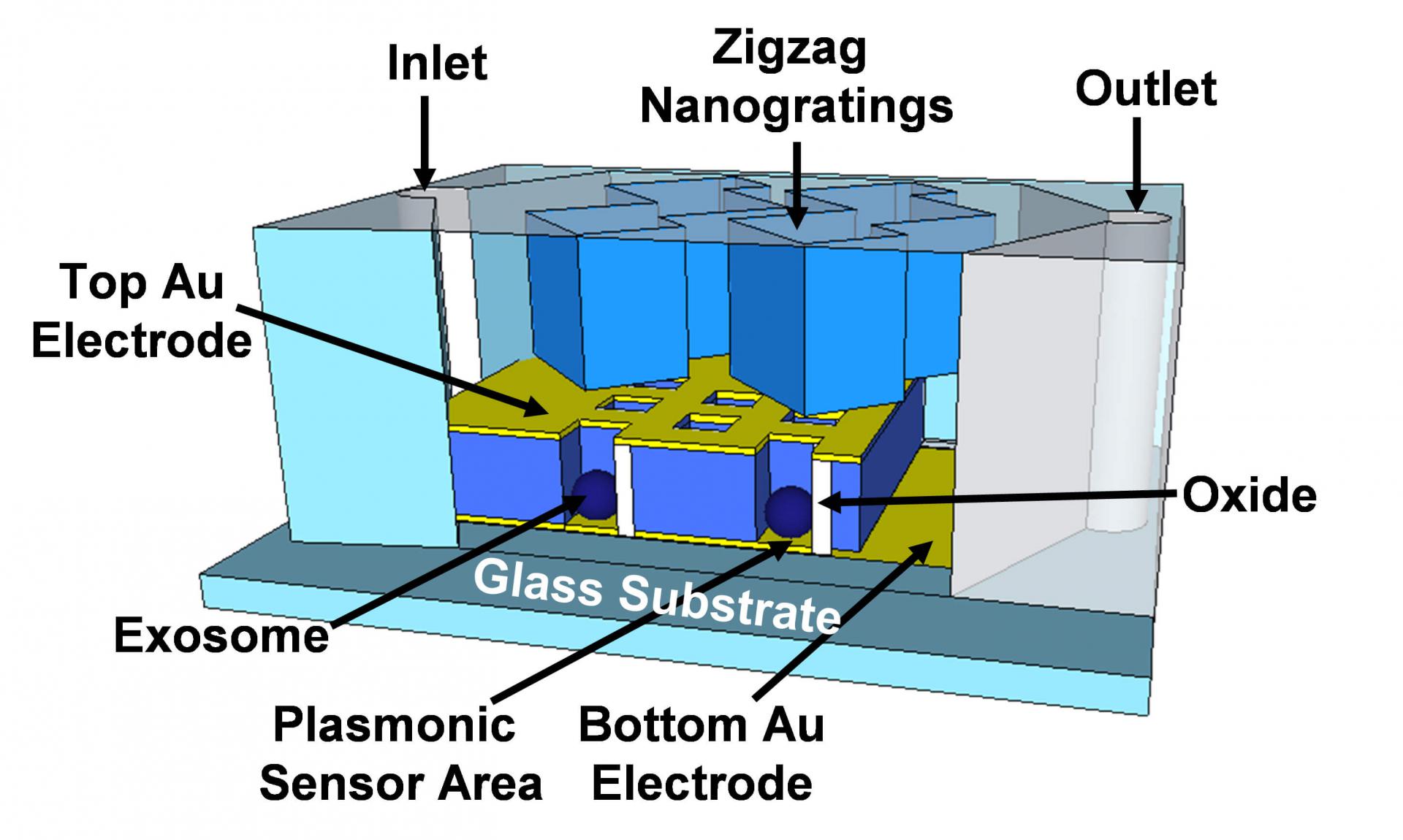 A Microfluidic Biosensing System for Improved Cancer Diagnostics and Screening
A Microfluidic Biosensing System for Improved Cancer Diagnostics and Screening -
 Rapid Electrophoretic Purification of Nucleic Acids Through a Proprietary Artificial Biochip
Rapid Electrophoretic Purification of Nucleic Acids Through a Proprietary Artificial Biochip -
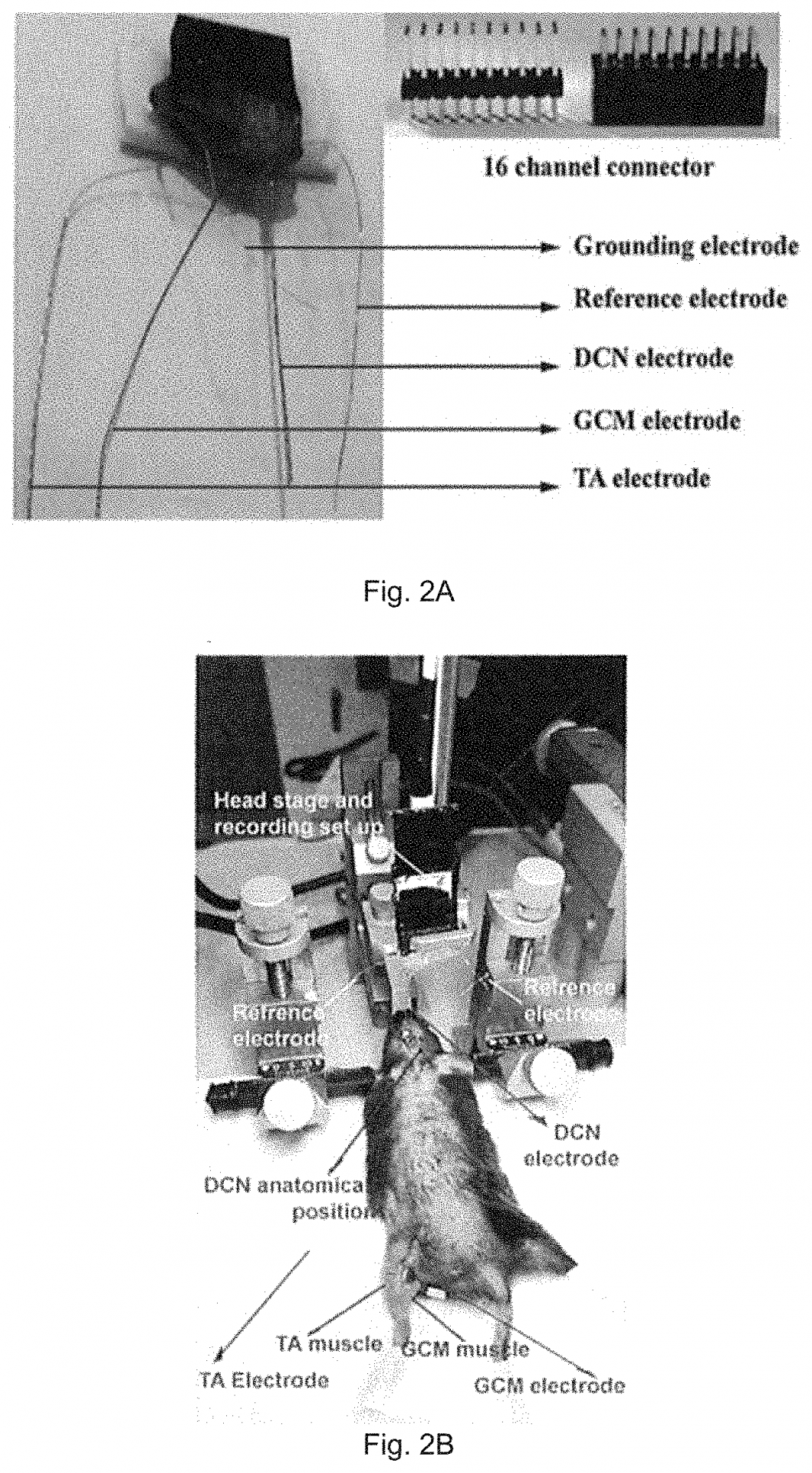 Neurostimulation System and Method for Modulating Abnormal Motor Movement
Neurostimulation System and Method for Modulating Abnormal Motor Movement -
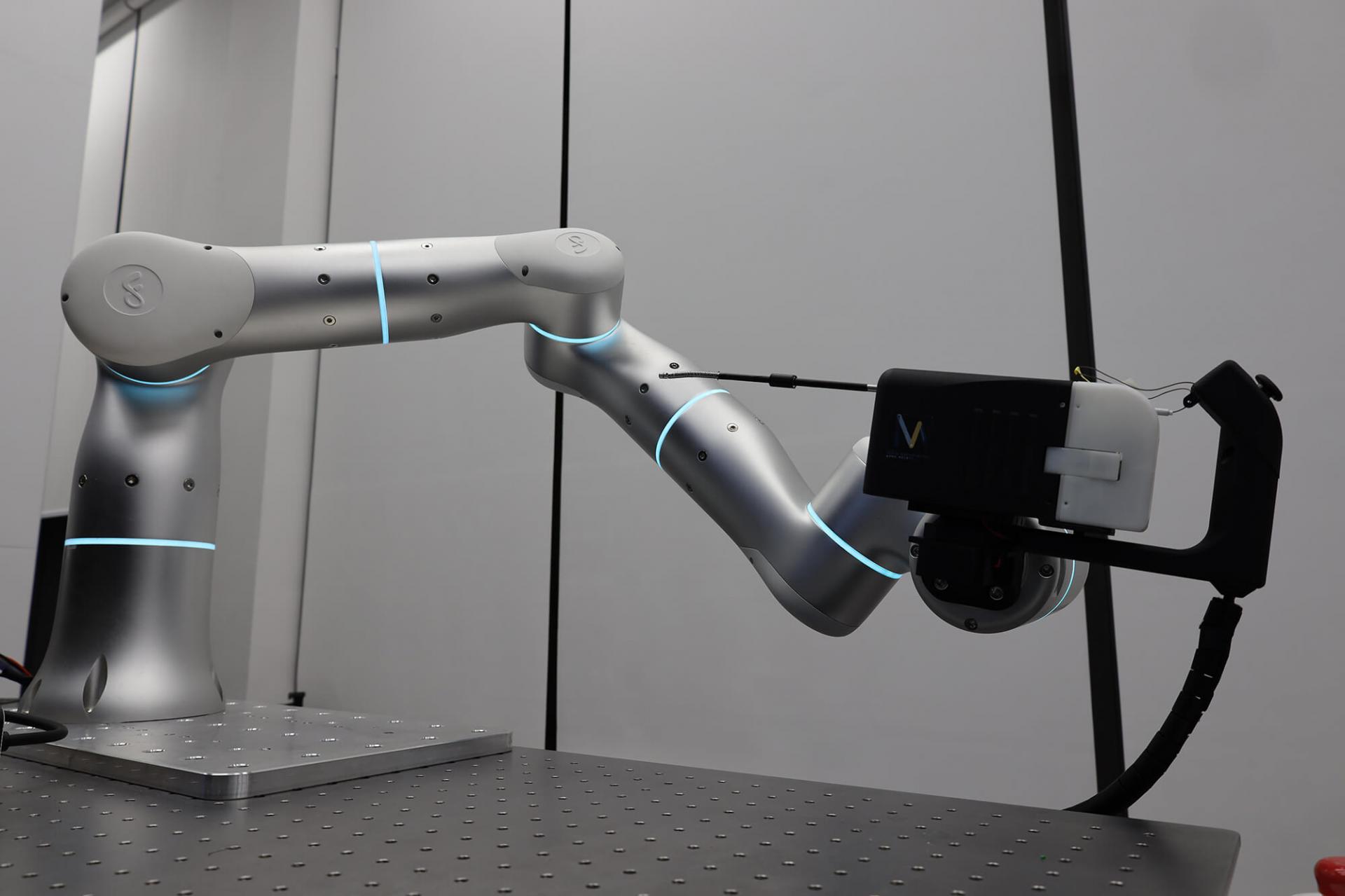 Hybrid-Structure Hand-Held Robotic Endoscope for Sinus Surgery
Hybrid-Structure Hand-Held Robotic Endoscope for Sinus Surgery -
 Asymmetric Competition Footwear for Hong Kong Olympic Fencing Team
Asymmetric Competition Footwear for Hong Kong Olympic Fencing Team -
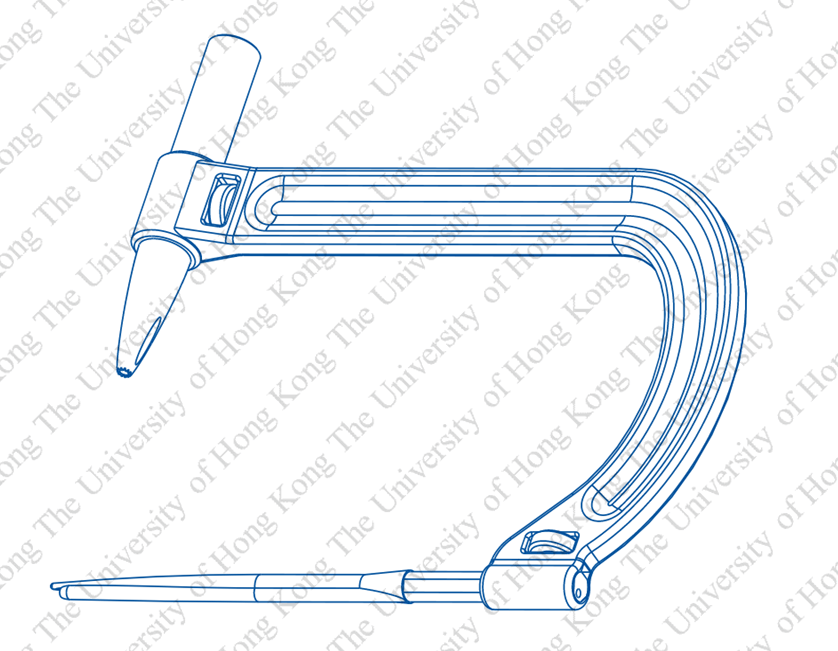 Simple precise placement guide for minimally invasive hip surgery
Simple precise placement guide for minimally invasive hip surgery -
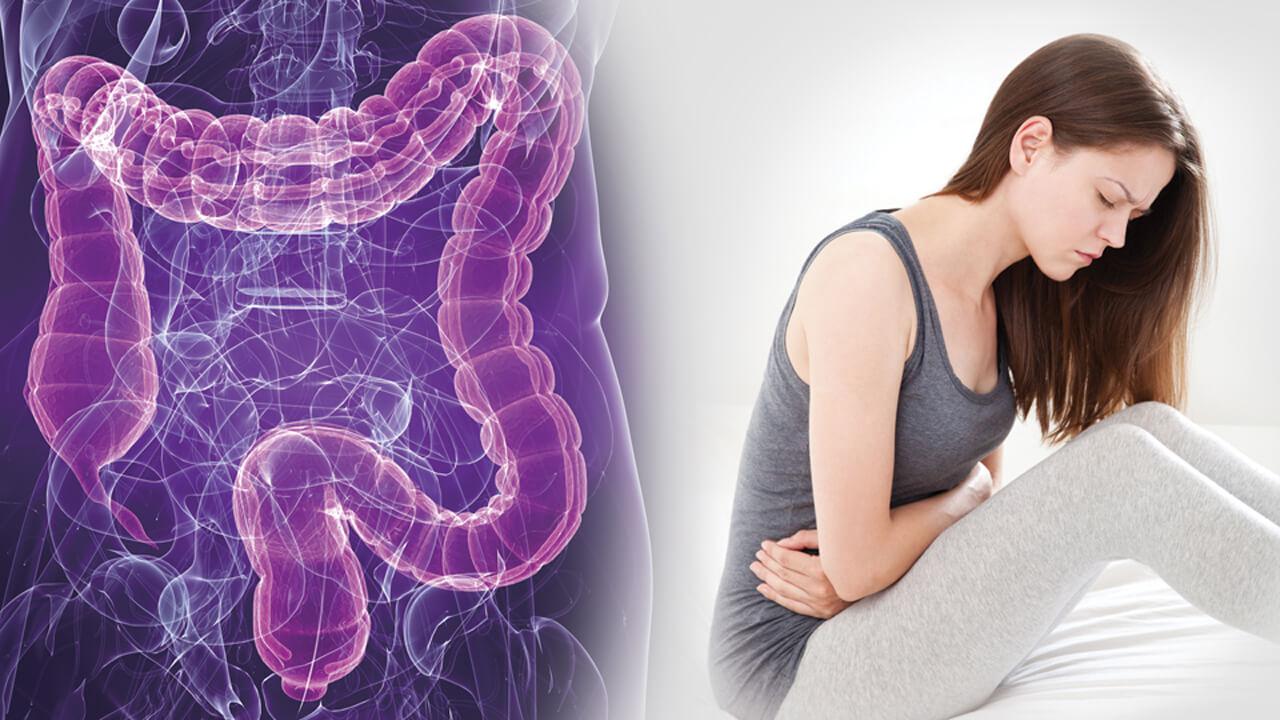 Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome -
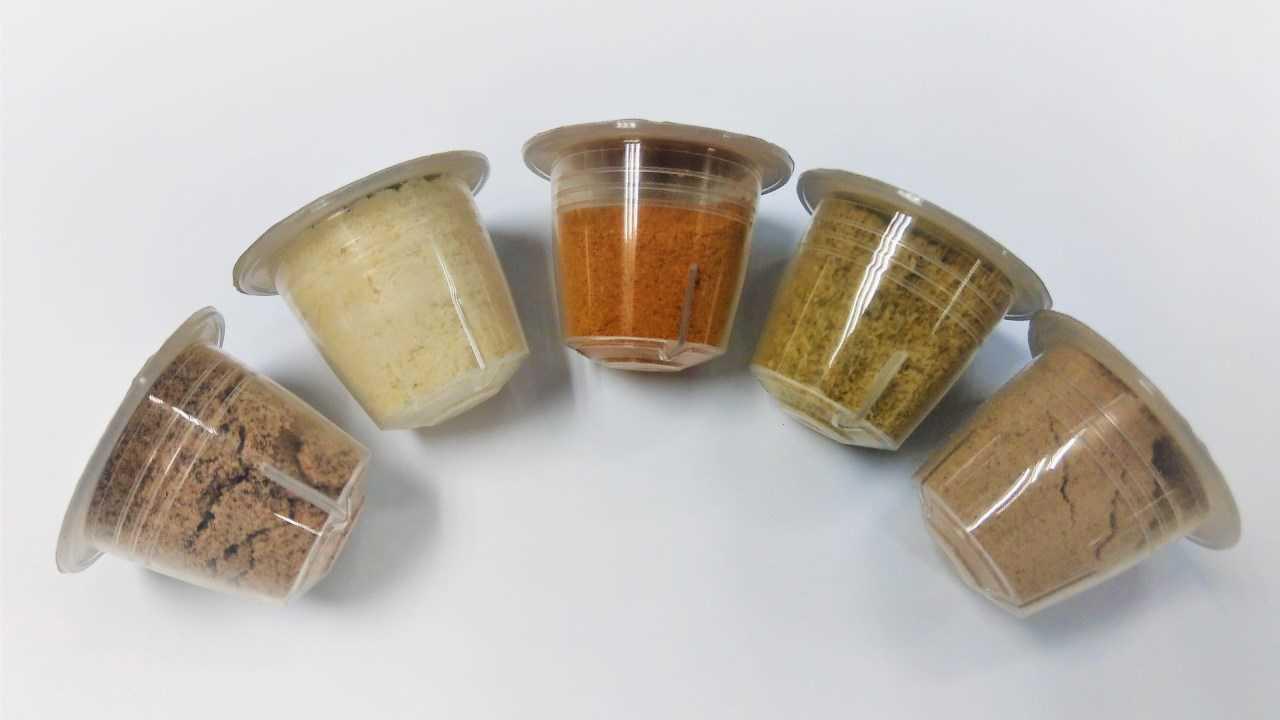 Nano-Herbal Capsules for Health and Wellness
Nano-Herbal Capsules for Health and Wellness -
 Novel Cocrystals of Dexamethasone
Novel Cocrystals of Dexamethasone -
 Early Language Prediction Technology
Early Language Prediction Technology -
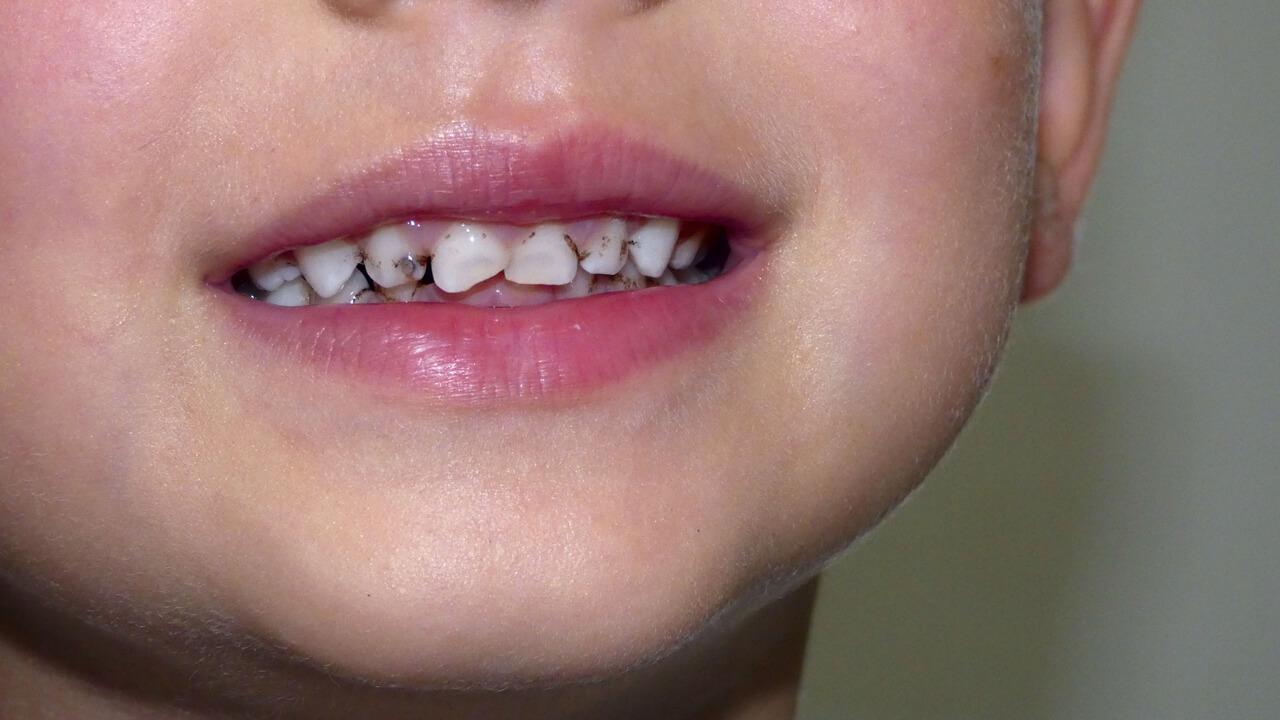 Novel Anti-microbial Agent for Preventing Dental Caries
Novel Anti-microbial Agent for Preventing Dental Caries -
 Novel Genome-editing Strategy for Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy
Novel Genome-editing Strategy for Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy -
 A Chinese Medicinal Formulation for Treating Inflammatory Bowel Disease
A Chinese Medicinal Formulation for Treating Inflammatory Bowel Disease -
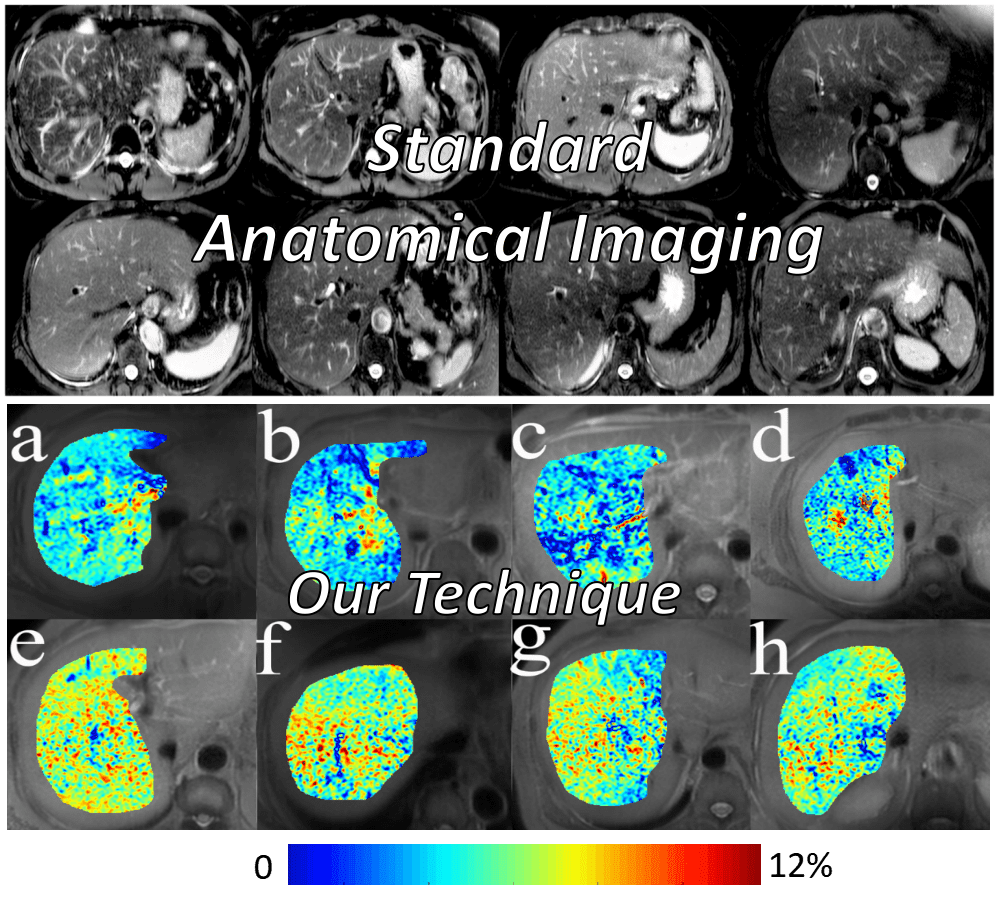 Non-invasive Biochemical Imaging of Human Tissues Using Spin-lock Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Non-invasive Biochemical Imaging of Human Tissues Using Spin-lock Magnetic Resonance Imaging -
 Smart Scar Care Pad (SSCP)
Smart Scar Care Pad (SSCP) -
 MY-O-Analyser
MY-O-Analyser -
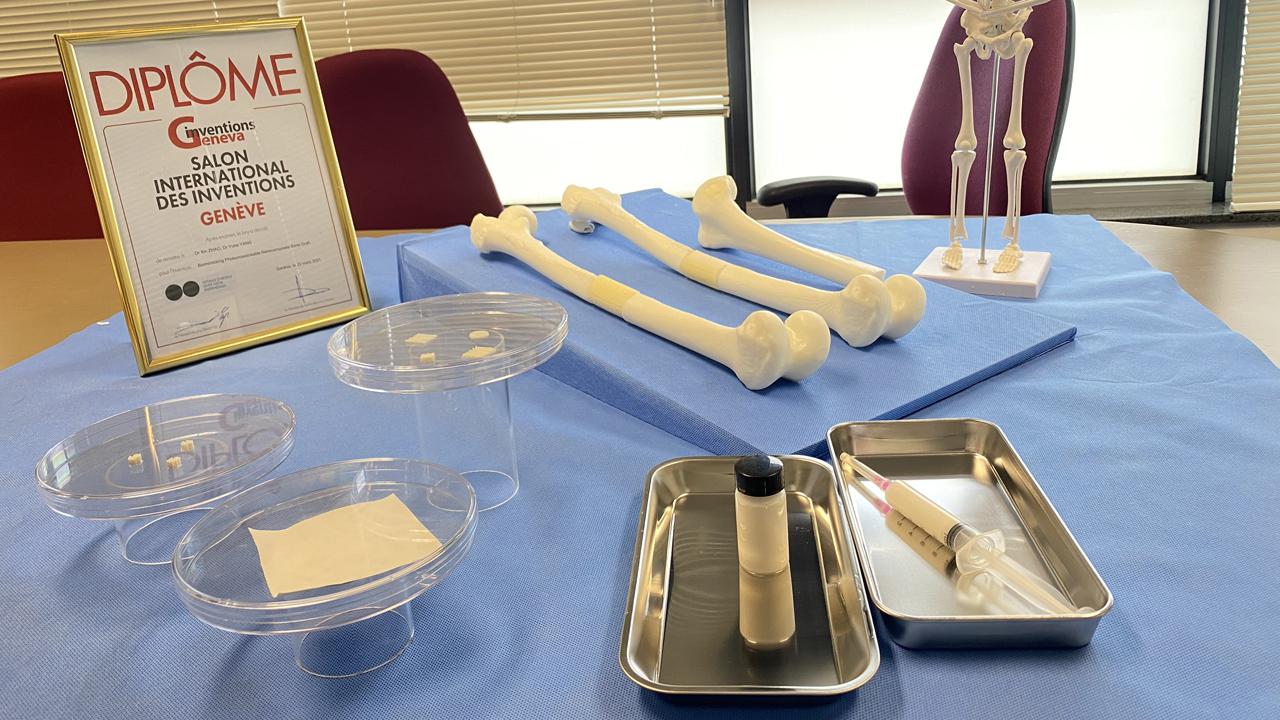 Biomimicking Photocrosslinkable Nanocomposite Bone Graft
Biomimicking Photocrosslinkable Nanocomposite Bone Graft -
 Green Functional Underwear for Elderly with Limited Mobility
Green Functional Underwear for Elderly with Limited Mobility -
 Flexible Endoluminal Soft Robot for GI Cancer Treatment
Flexible Endoluminal Soft Robot for GI Cancer Treatment -
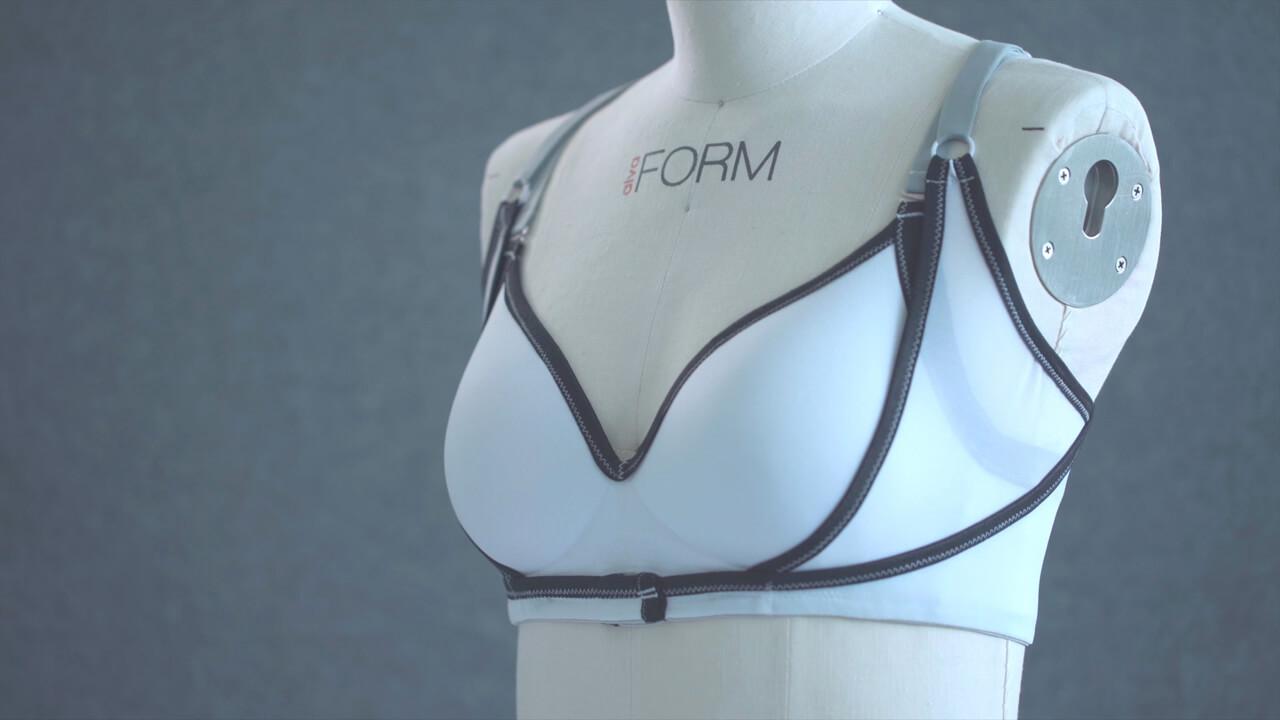 A Customised Comfort Bra to Aid Recovery from Mastectomy
A Customised Comfort Bra to Aid Recovery from Mastectomy -
 Pharmaceutical composition with anti-colorectal cancer effect and application thereof
Pharmaceutical composition with anti-colorectal cancer effect and application thereof -
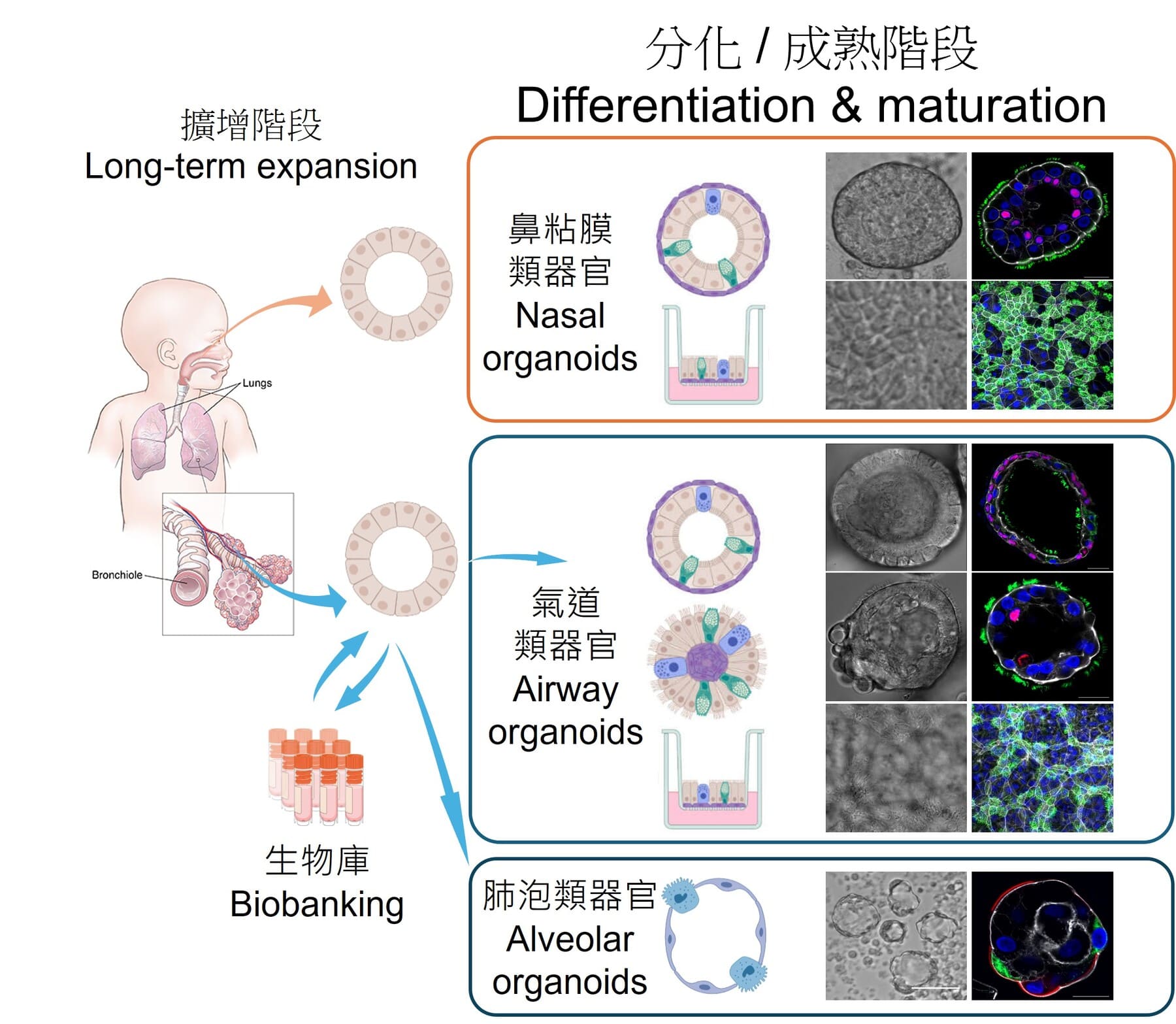 Comprehensive Human Respiratory Organoid Technology Platform
Comprehensive Human Respiratory Organoid Technology Platform -
 iMeddy
iMeddy -
 Nano-vesicles for Improving Drug’s Stability and Efficacy to Treat Chronic Diseases
Nano-vesicles for Improving Drug’s Stability and Efficacy to Treat Chronic Diseases -
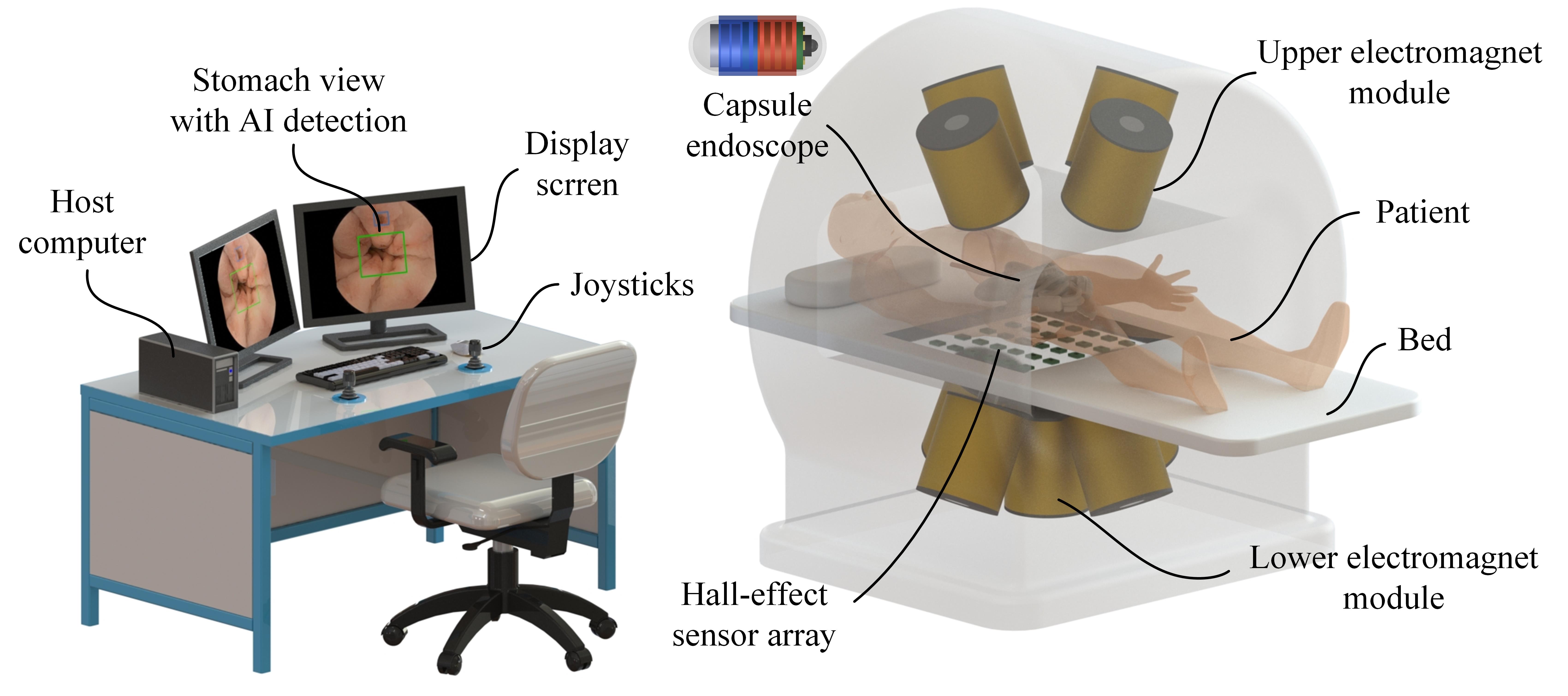 An automatic stomach screening method using magnetically actuated capsule endoscope
An automatic stomach screening method using magnetically actuated capsule endoscope -
 Depression subtyping
Depression subtyping -
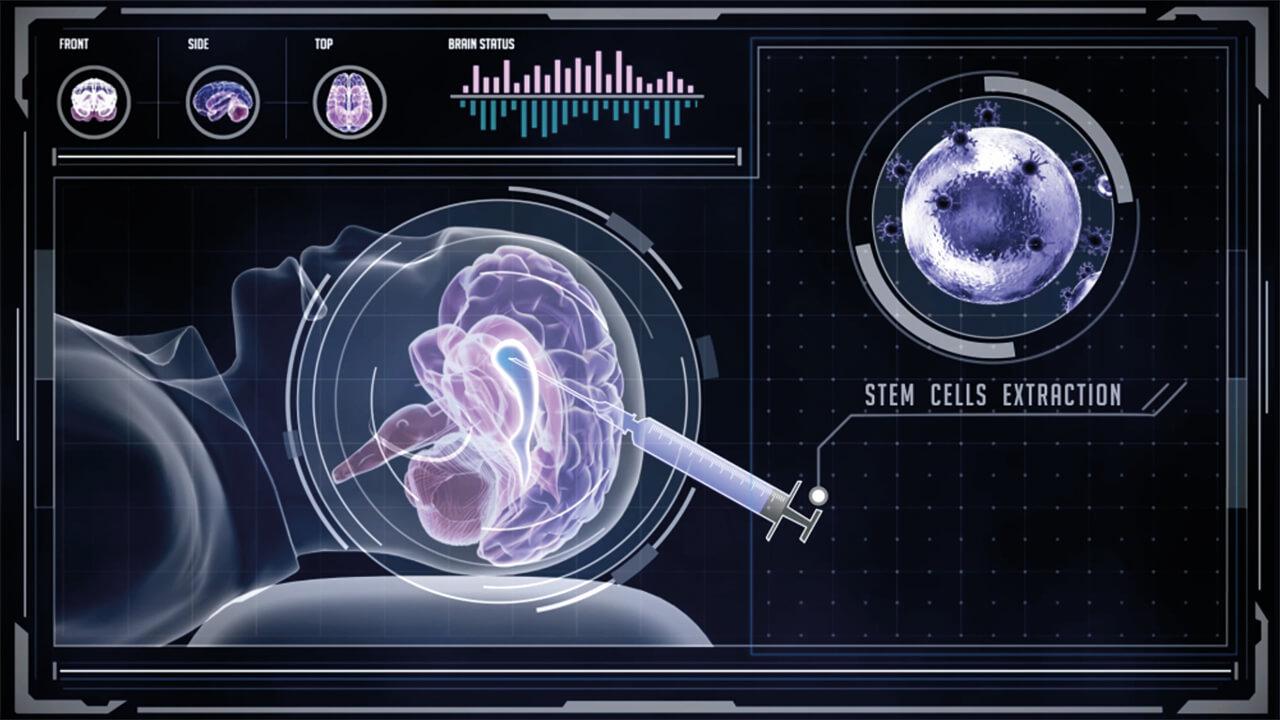 Extracting Autologous Neural Stem Cells for Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Extracting Autologous Neural Stem Cells for Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases -
 Cancer Catcher - Early Detection of Circulating Tumour Cells
Cancer Catcher - Early Detection of Circulating Tumour Cells -
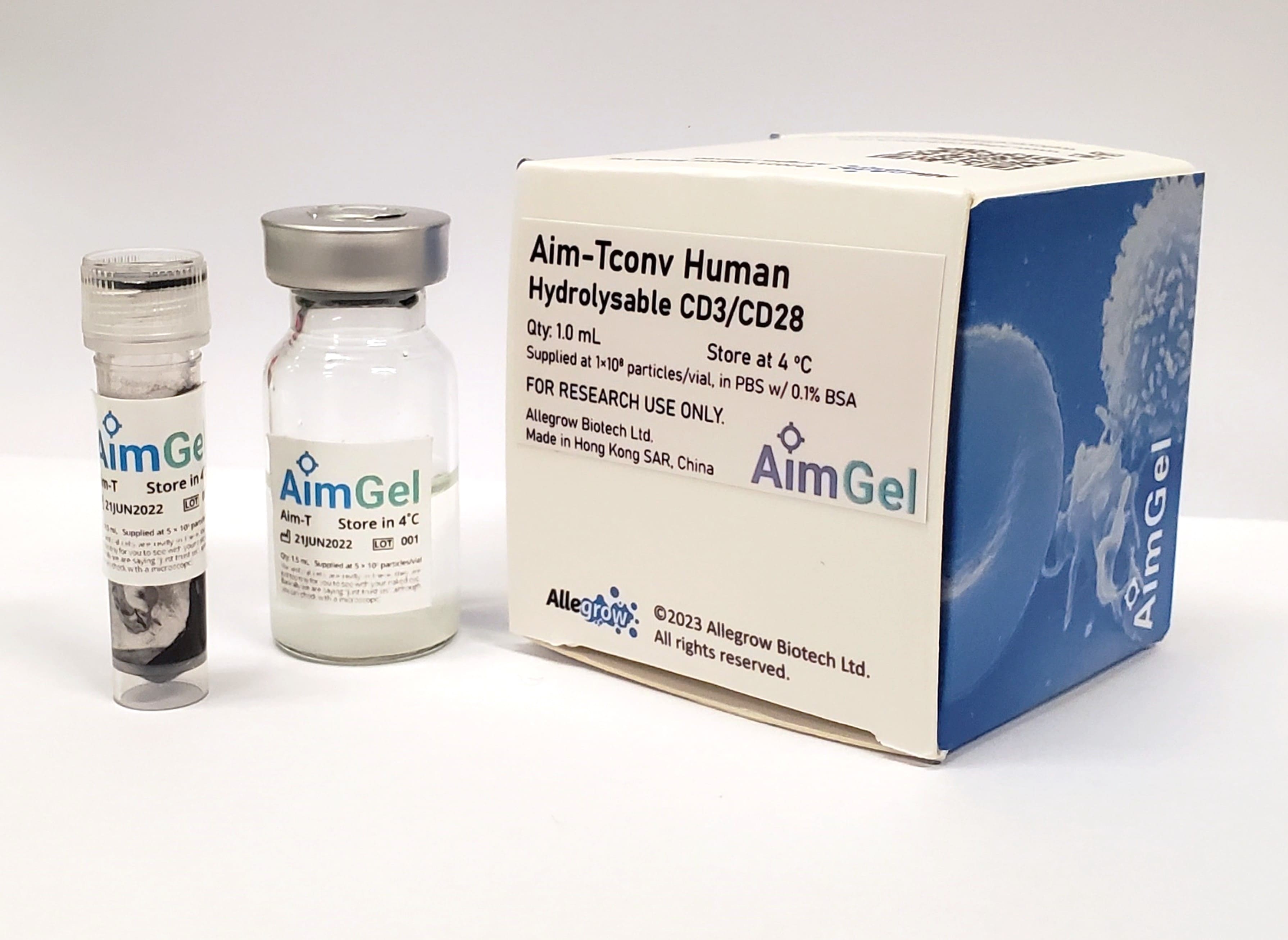 AimGel: Supercharing Cell Therapy Production and Development
AimGel: Supercharing Cell Therapy Production and Development -
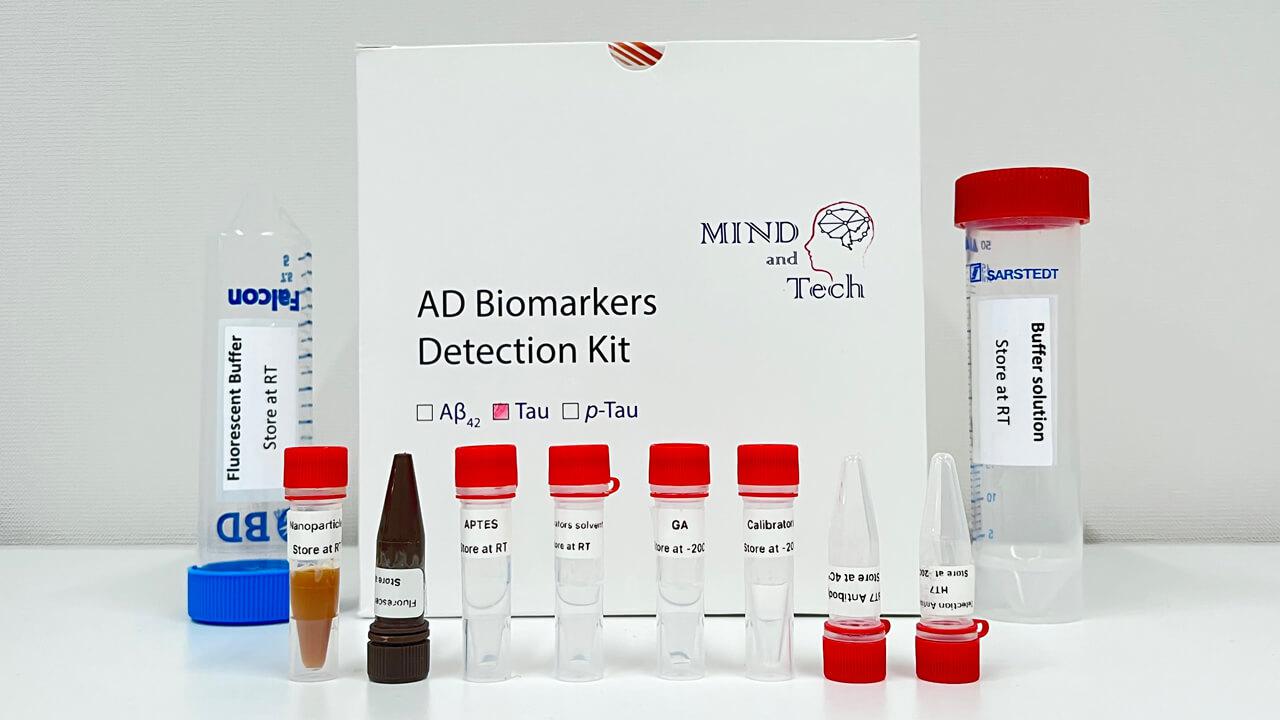 Non-invasive detection kit for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
Non-invasive detection kit for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease -
 A modified Chinese Medicine formulation for treating Alzheimer's disease
A modified Chinese Medicine formulation for treating Alzheimer's disease -
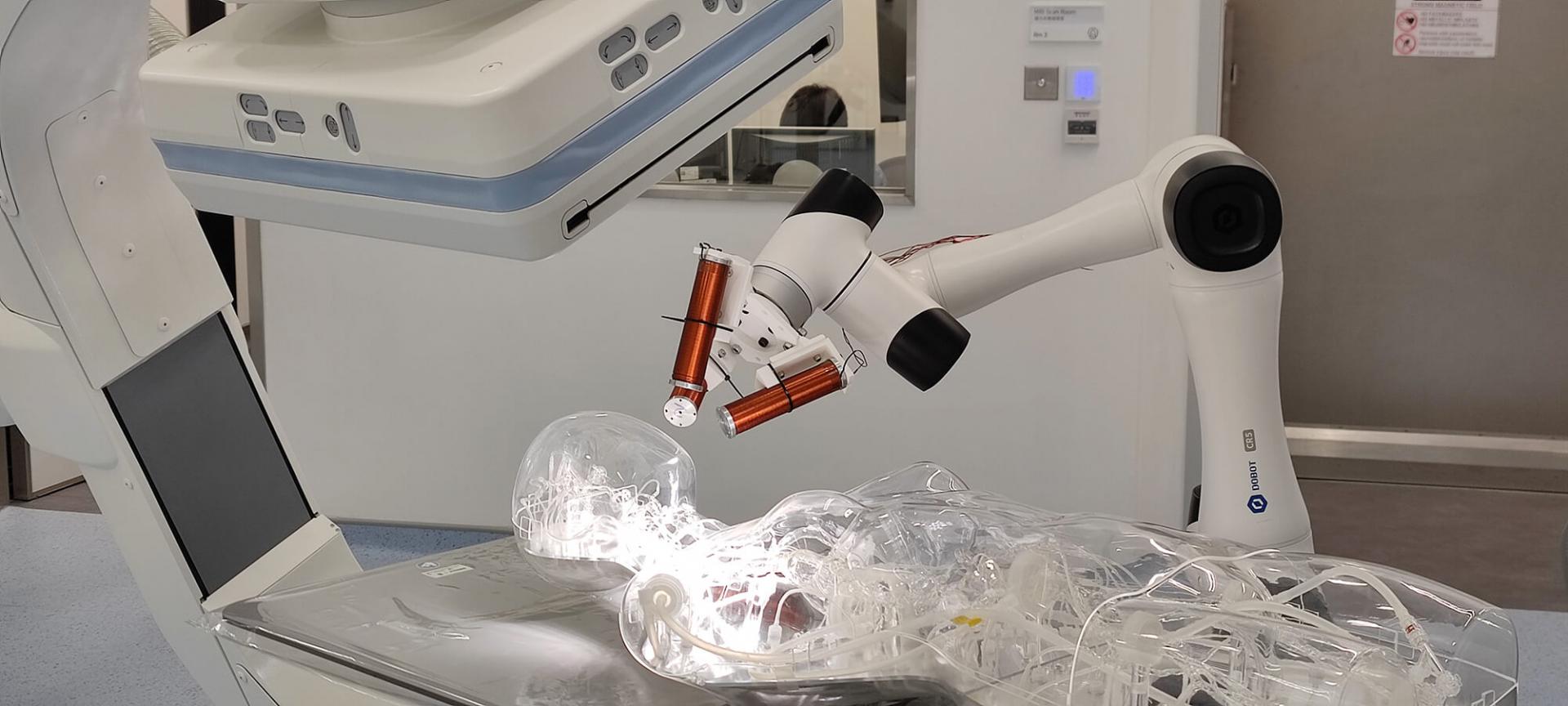 Microrobotic platform for the image-guided endovascular intervention
Microrobotic platform for the image-guided endovascular intervention -
 Liverscan
Liverscan -
 Antiviral Hydrophobic Surfaces via Laser-Structured Copper Nanoparticles
Antiviral Hydrophobic Surfaces via Laser-Structured Copper Nanoparticles -
 Tuberculatin analogs as antiviral agents
Tuberculatin analogs as antiviral agents -
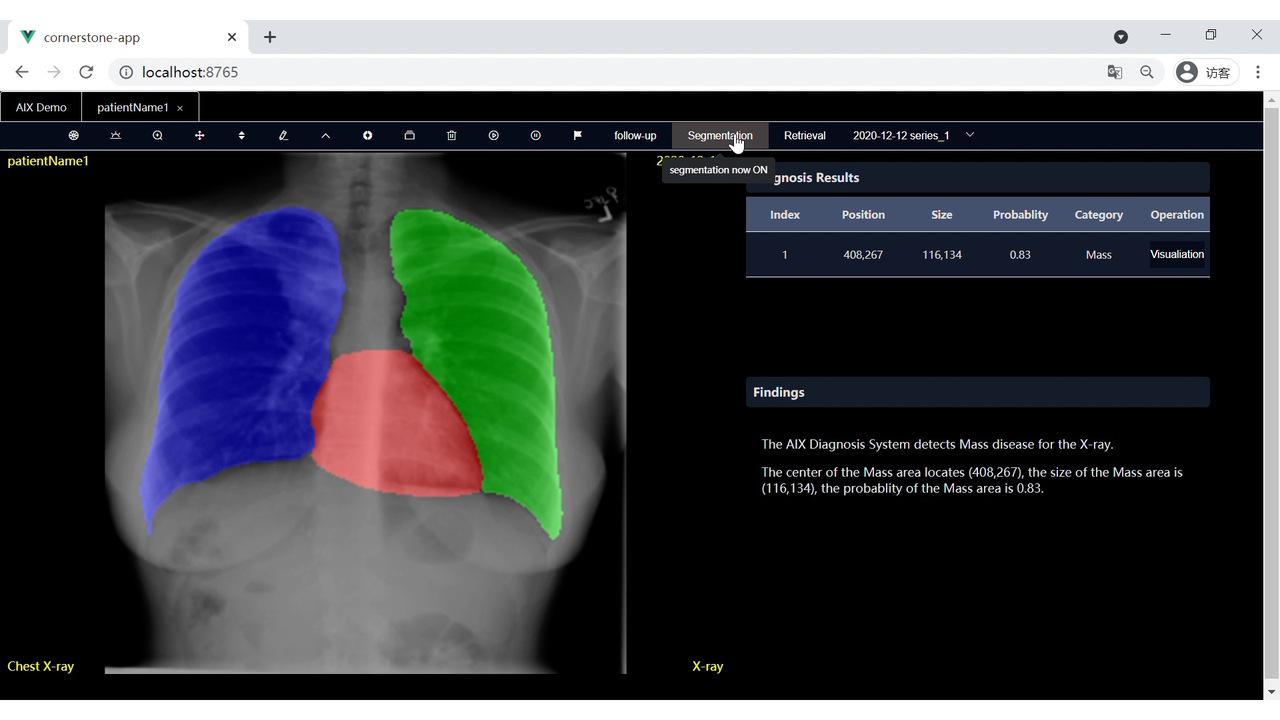 「AIX」Chest X-ray Screening with AI
「AIX」Chest X-ray Screening with AI -
 MTOR-independent activator of TFEB for autophagy enhancement and uses thereof
MTOR-independent activator of TFEB for autophagy enhancement and uses thereof -
 One stool test for multiple human disease early detection
One stool test for multiple human disease early detection -
 Advanced Catalytic Material for Air Purification
Advanced Catalytic Material for Air Purification -
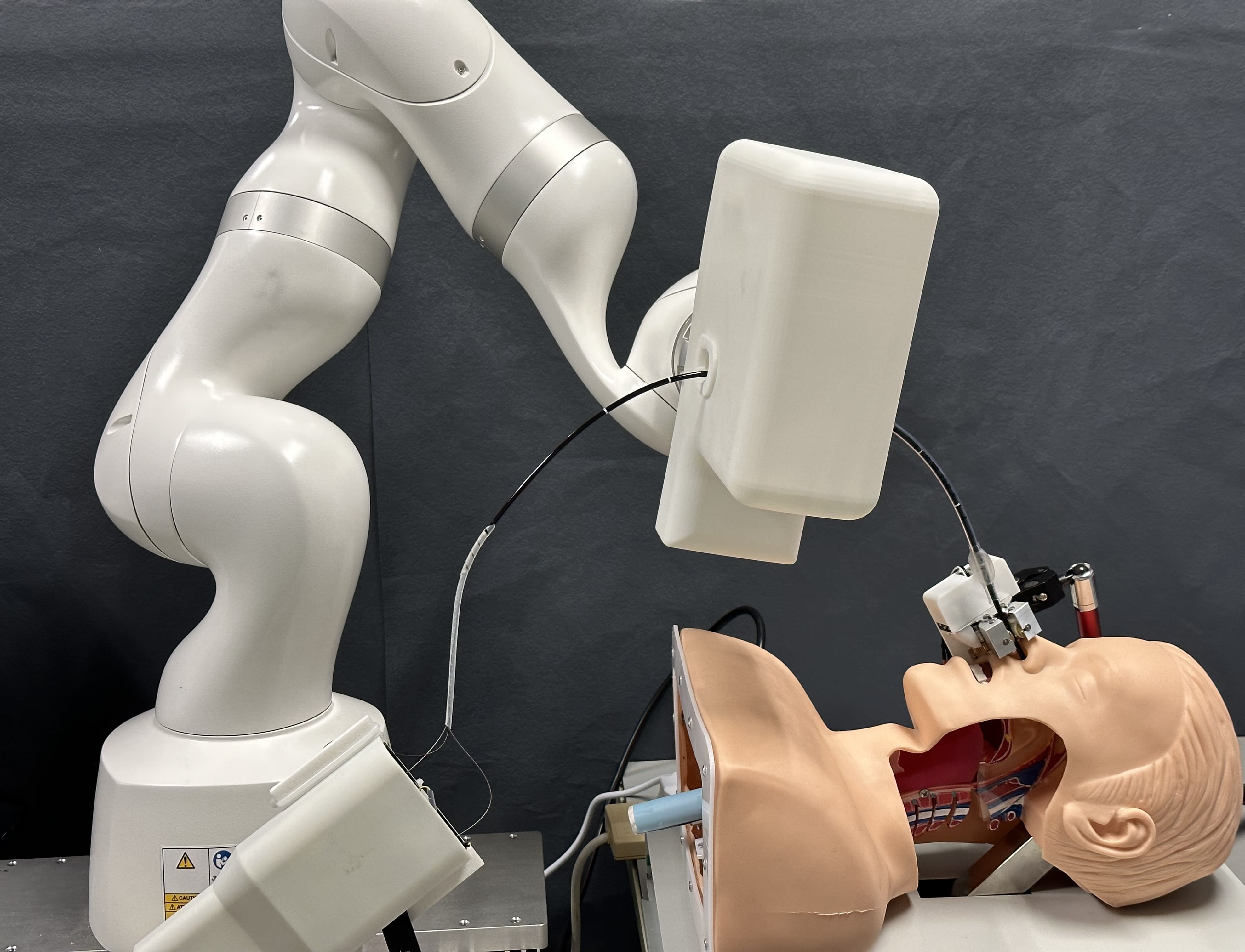 A Vision-Guided Nasotracheal Intubation Robot
A Vision-Guided Nasotracheal Intubation Robot -
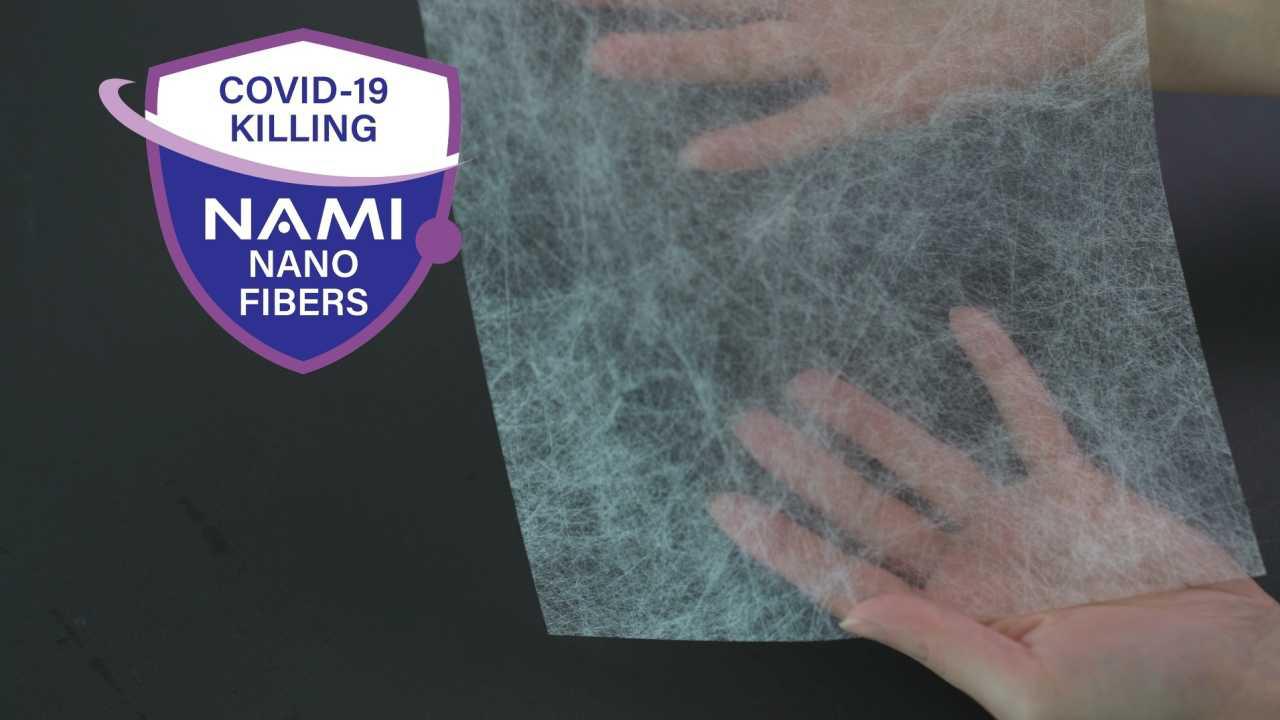 COVID-19 Virus-Killing Nanofiber Materials
COVID-19 Virus-Killing Nanofiber Materials -
 Microrobotic platform for the image-guided endovascular intervention
Microrobotic platform for the image-guided endovascular intervention -
 Anti-leakage surgical kit with noval therapeutic high GAG biomaterial
Anti-leakage surgical kit with noval therapeutic high GAG biomaterial -
 Growth Factor-free Proliferation & Differentiation of Stem Cell
Growth Factor-free Proliferation & Differentiation of Stem Cell -
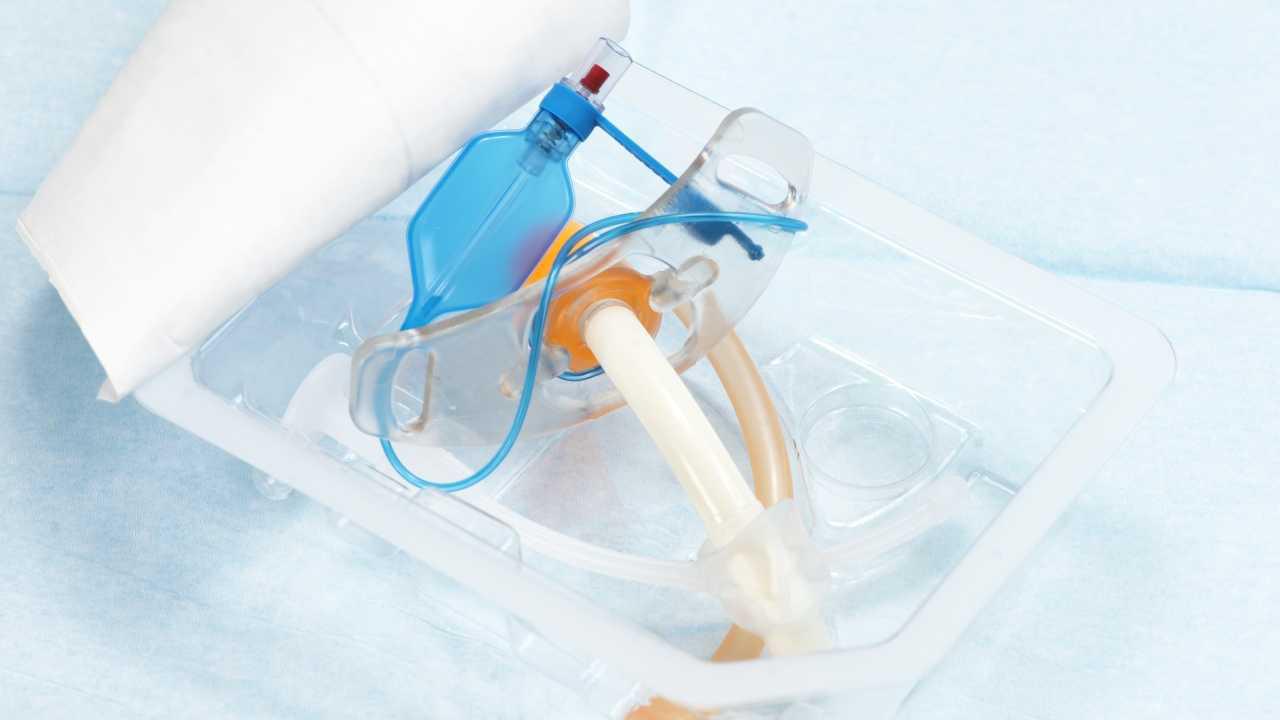 Antifouling Germ-Spike Technology
Antifouling Germ-Spike Technology -
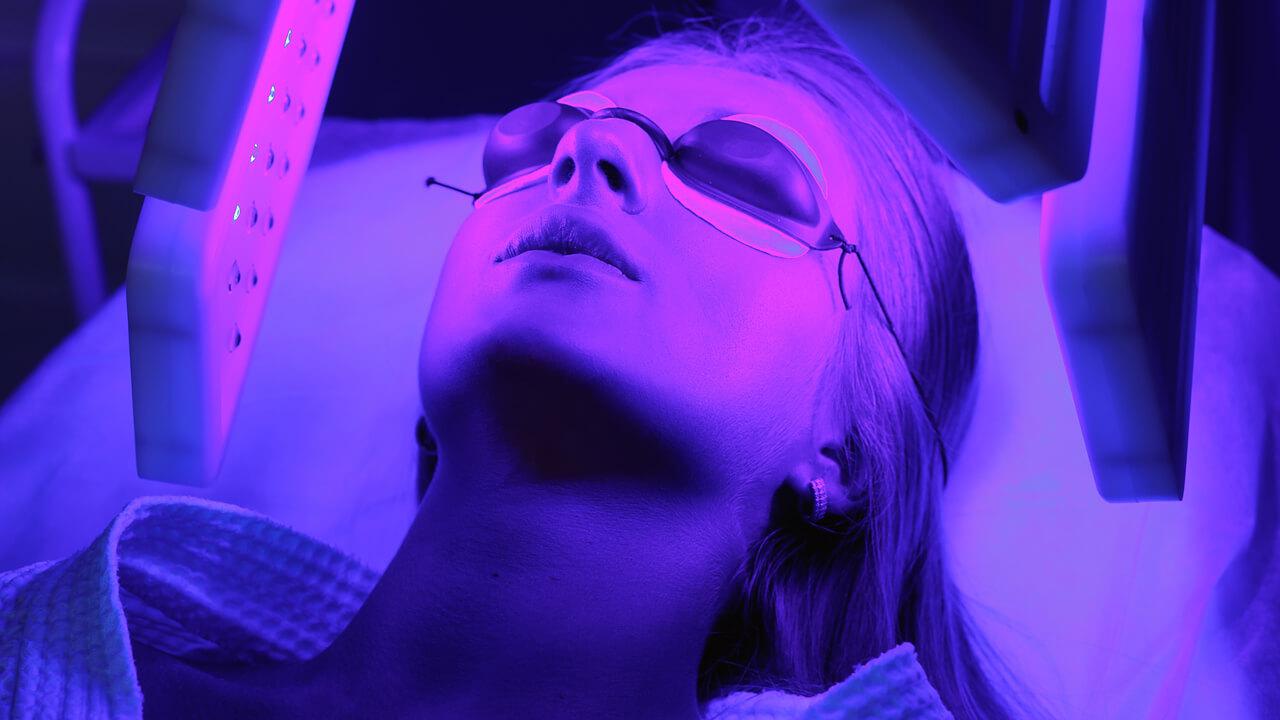 Novel Drug for Cancer Diagnostics and Photodynamic Treatment
Novel Drug for Cancer Diagnostics and Photodynamic Treatment -
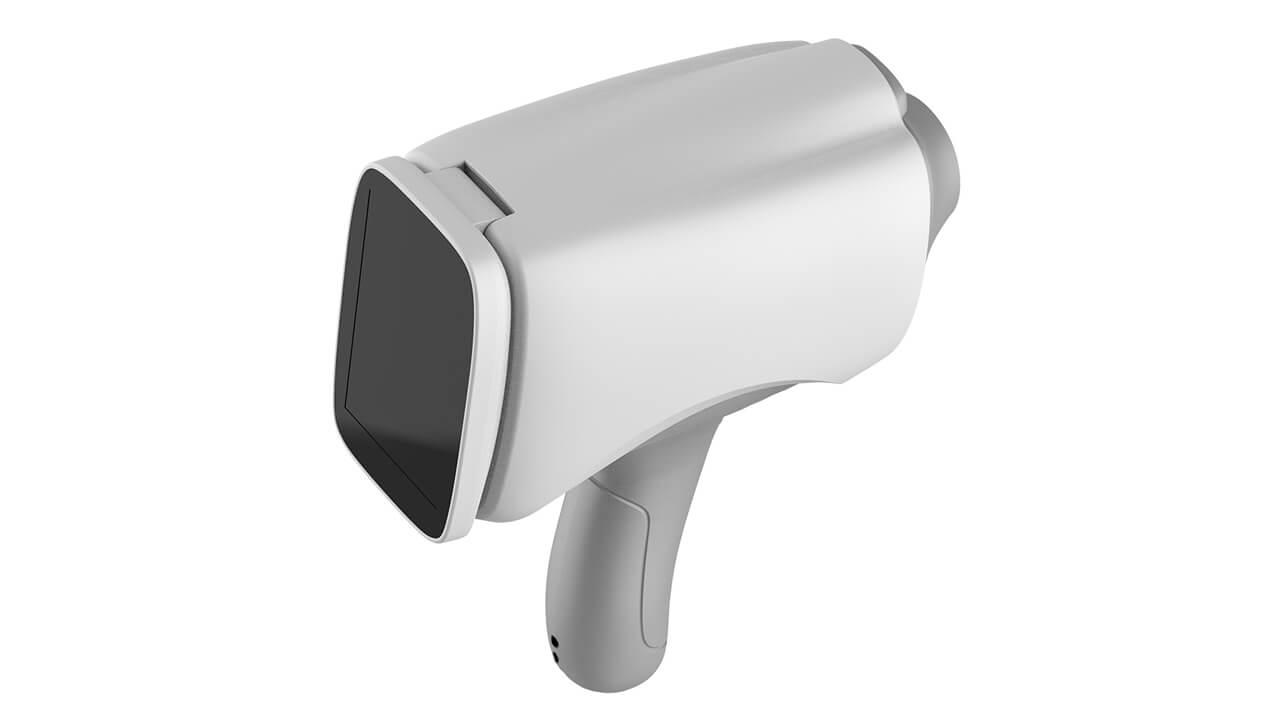 Corneal topographer, OK lens and fitting software for OK lens.
Corneal topographer, OK lens and fitting software for OK lens. -
![Long COVID Test: [Non-Invasive Stool Test to detect distinct gut microbiome profile associated with “Long COVID”]](/uploads/image/202304/6802a81a4ec6afc2ac97f3912ec9a7f4.jpg) Long COVID Test: [Non-Invasive Stool Test to detect distinct gut microbiome profile associated with “Long COVID”]
Long COVID Test: [Non-Invasive Stool Test to detect distinct gut microbiome profile associated with “Long COVID”] -
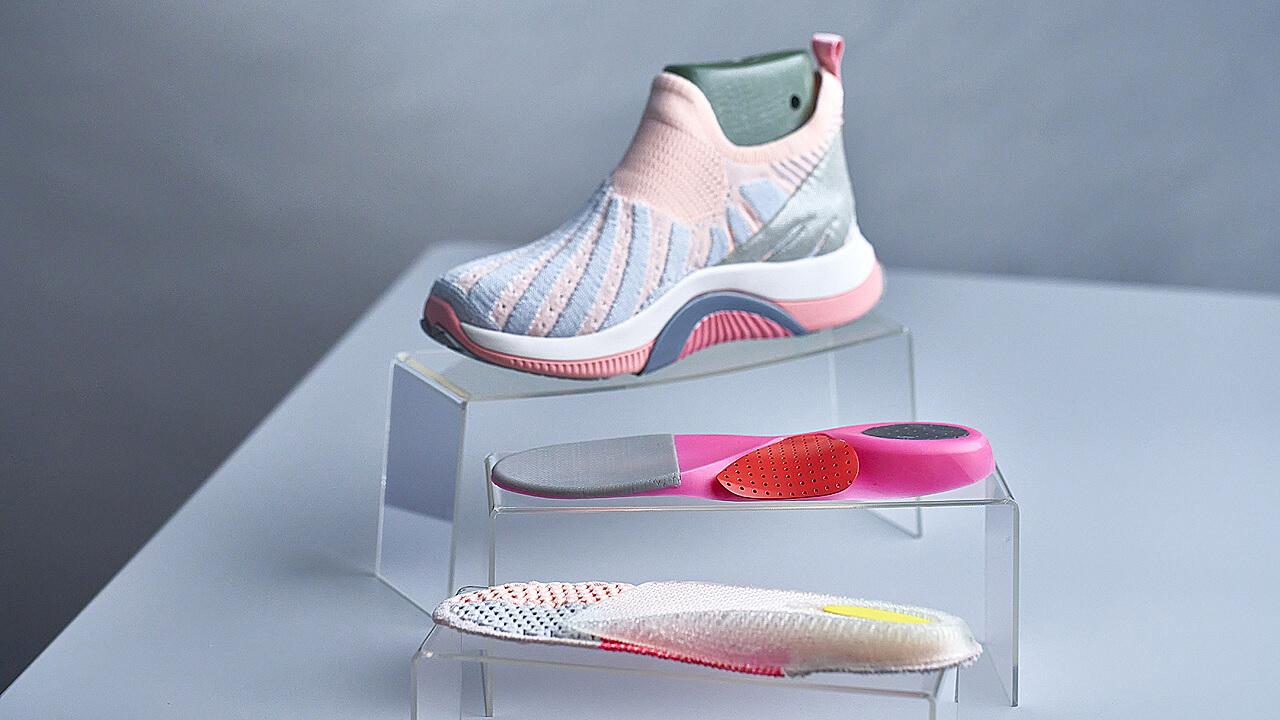 Bionic Smart and Functional Footwear System for Pregnant Woman
Bionic Smart and Functional Footwear System for Pregnant Woman -
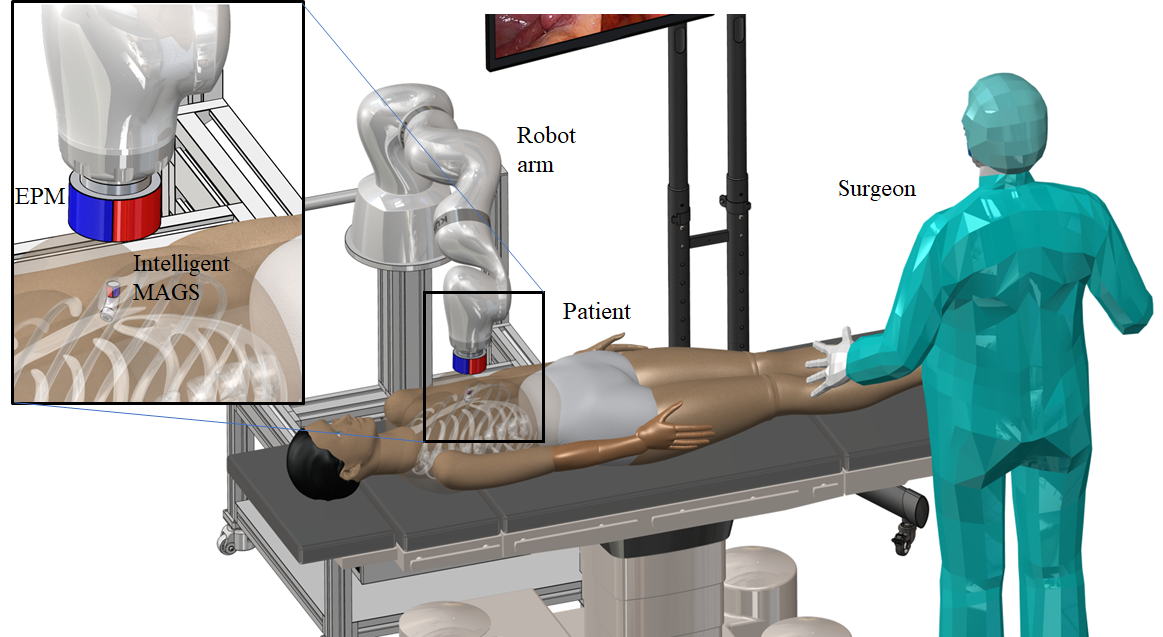 Magnetic Anchored and Guided Endoscope (MAGS) for Single Incision Surgery
Magnetic Anchored and Guided Endoscope (MAGS) for Single Incision Surgery -
 Microrobotic system with actuation and imaging sintegrated for Knee joint repair
Microrobotic system with actuation and imaging sintegrated for Knee joint repair -
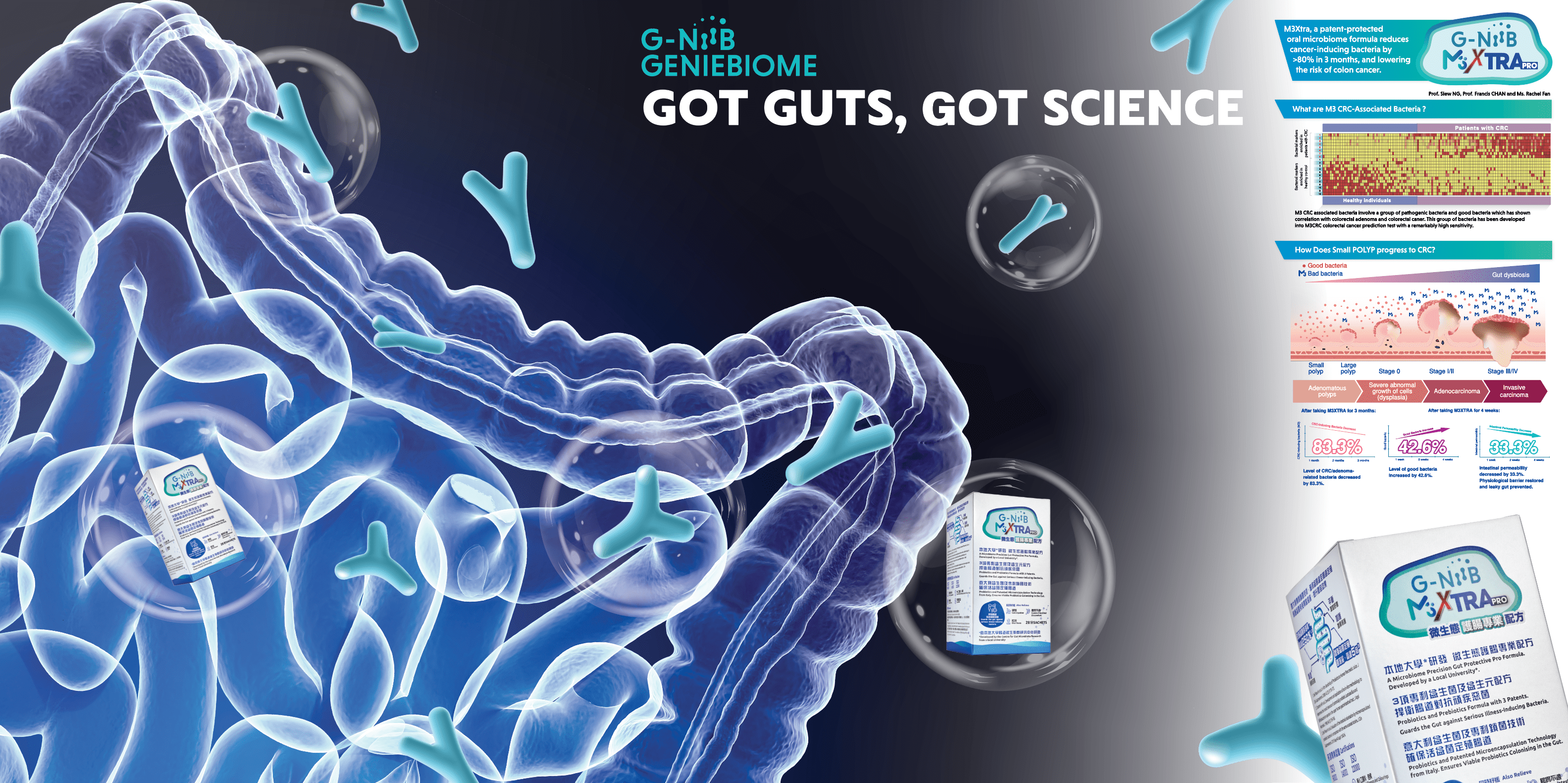 M3Xtra PRO
M3Xtra PRO -
 Skin Whitening, Anti-aging and Skin Care Product
Skin Whitening, Anti-aging and Skin Care Product -
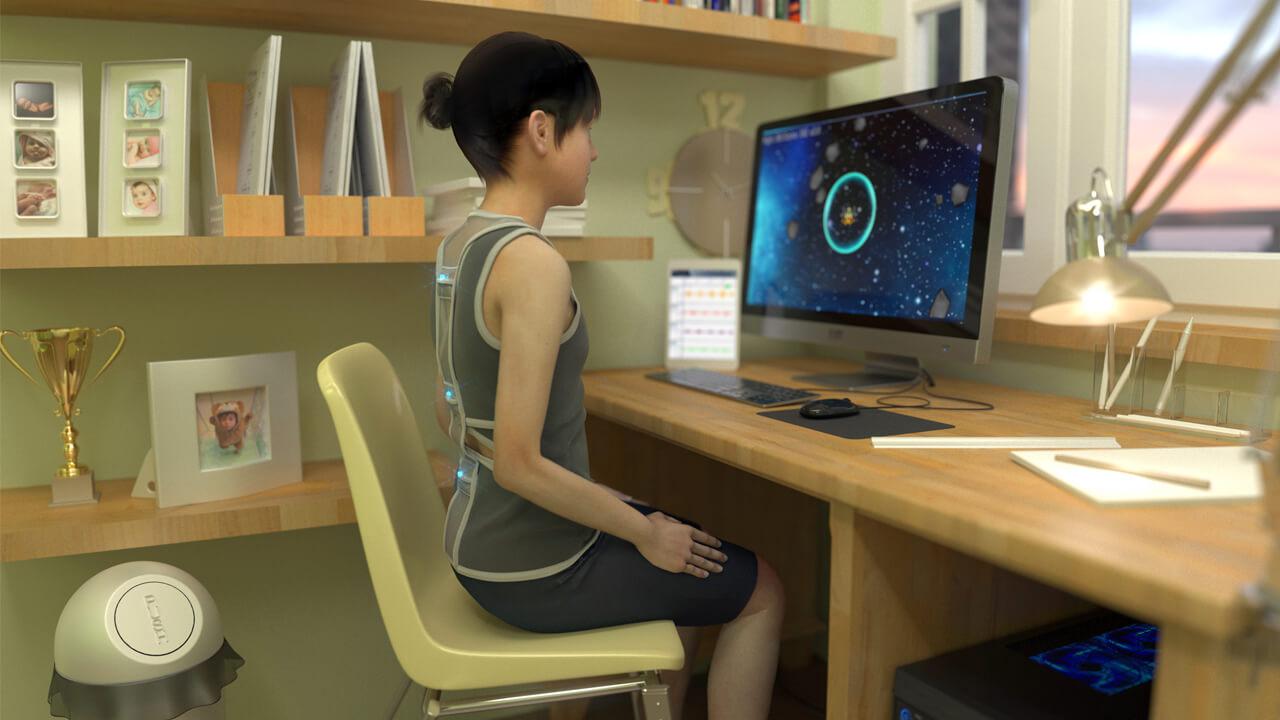 Biofeedback System with Body Mapping Clothing for Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
Biofeedback System with Body Mapping Clothing for Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis -
 High-Intensity Narrow-Wavelength Light Disinfection
High-Intensity Narrow-Wavelength Light Disinfection -
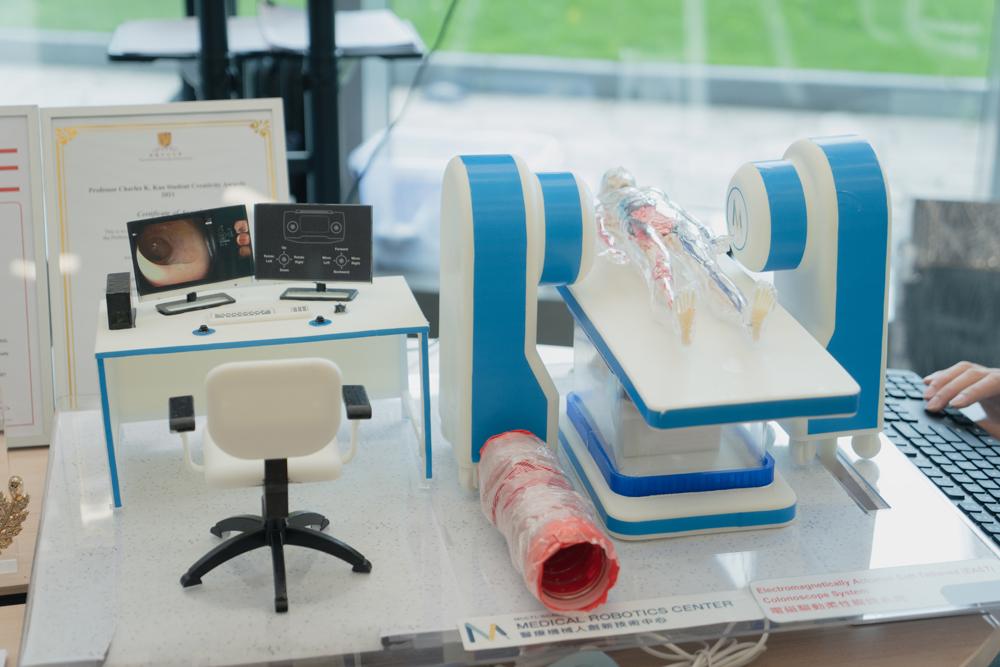 Magnetic-guided Soft Tethered Capsule Endoscope for Upper/Lower GI Diagnostic
Magnetic-guided Soft Tethered Capsule Endoscope for Upper/Lower GI Diagnostic -
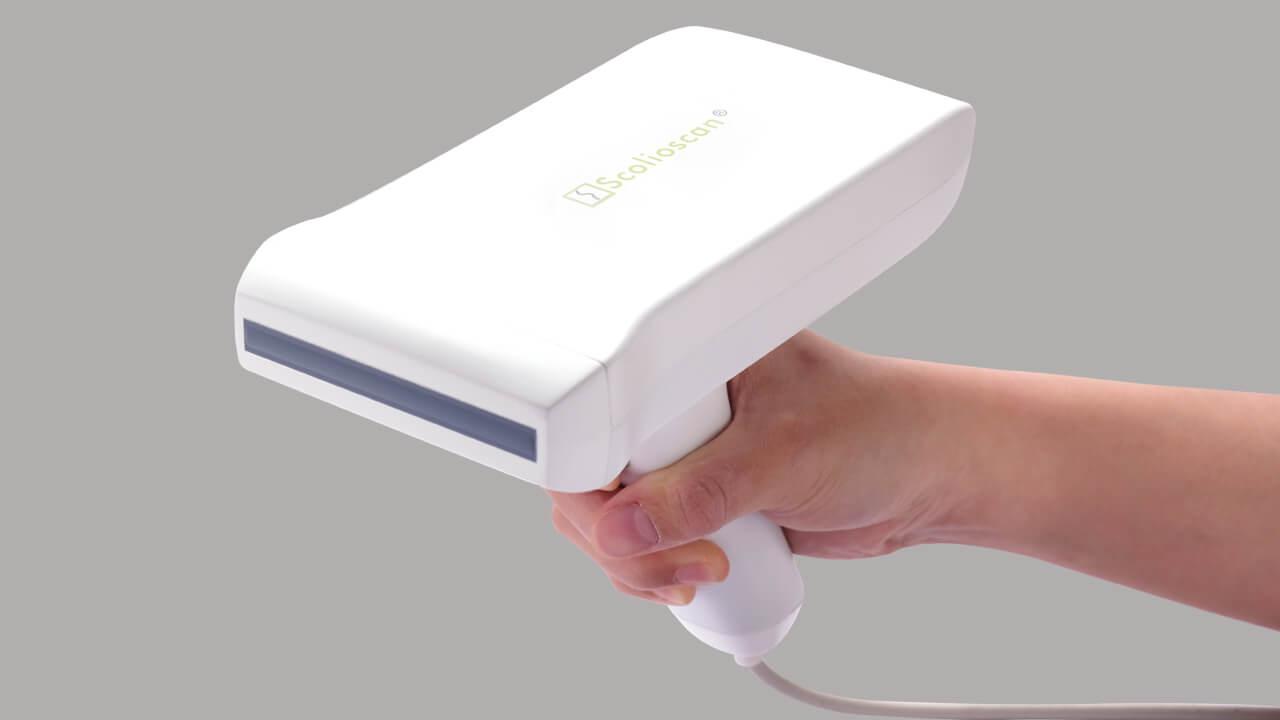 Scolioscan - 3D Ultrasound Scoliosis Assessment System
Scolioscan - 3D Ultrasound Scoliosis Assessment System -
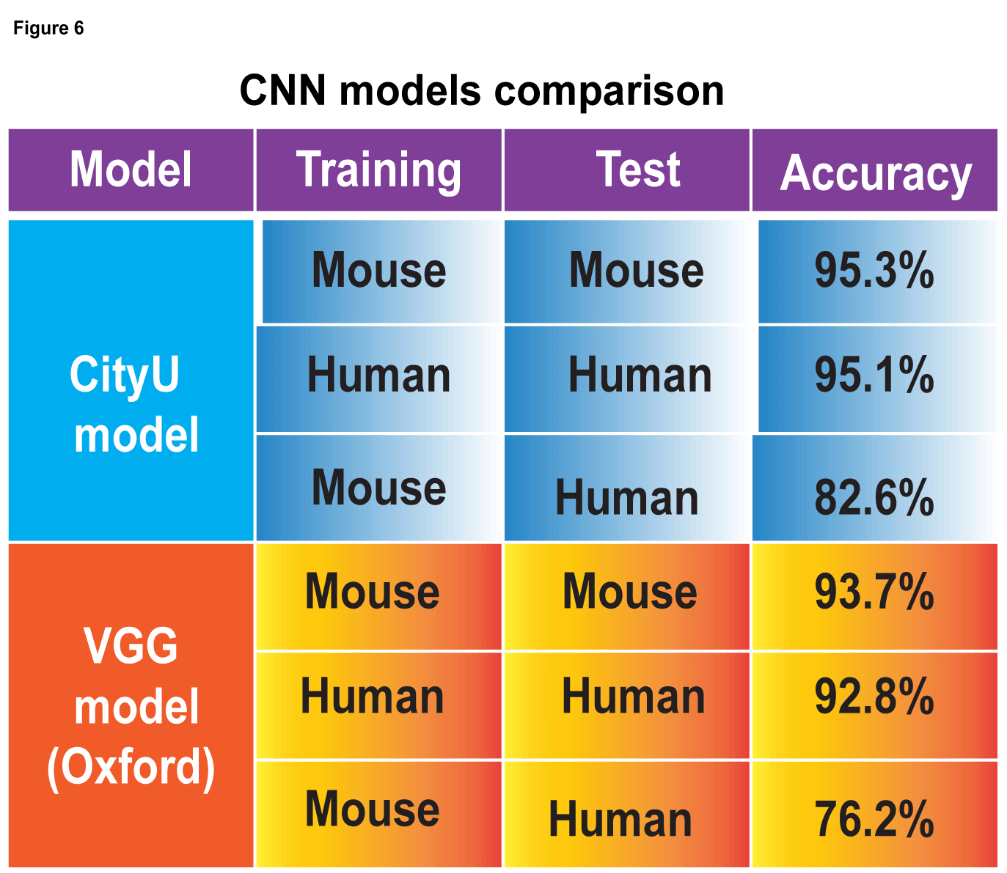 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Electrocephalogram (EEG)-based Drug's Screening Platform
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Electrocephalogram (EEG)-based Drug's Screening Platform -
 AI-aided Medical Image Analytics for Early Cancer Screening
AI-aided Medical Image Analytics for Early Cancer Screening -
 Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease Using Corynoxine B
Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease Using Corynoxine B -
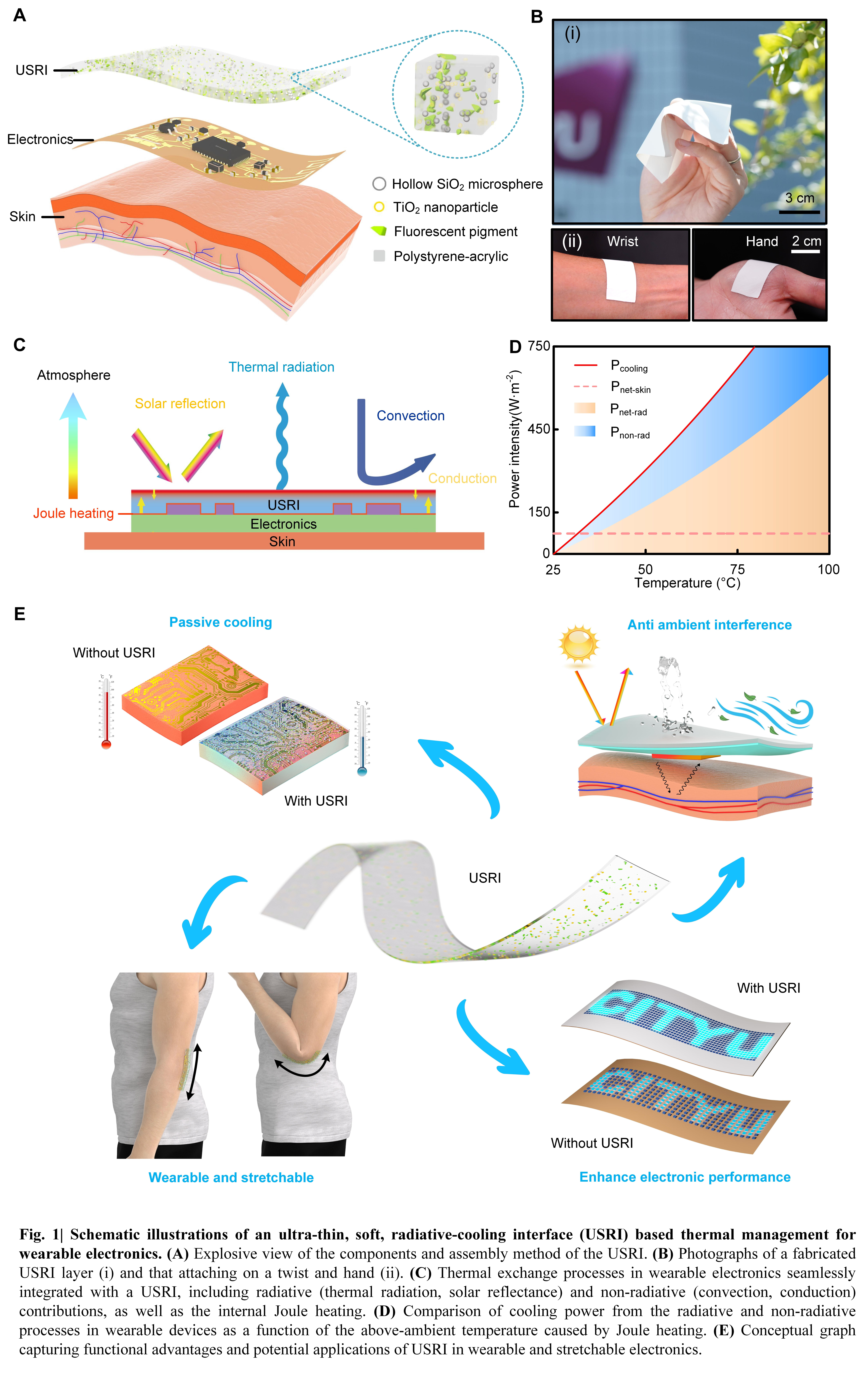 Cooling Technology for Epidermal Electronics
Cooling Technology for Epidermal Electronics -
 Vitogram®: Digital health innovation for telemedicine
Vitogram®: Digital health innovation for telemedicine -
 Pleryon Therapeutics
Pleryon Therapeutics -
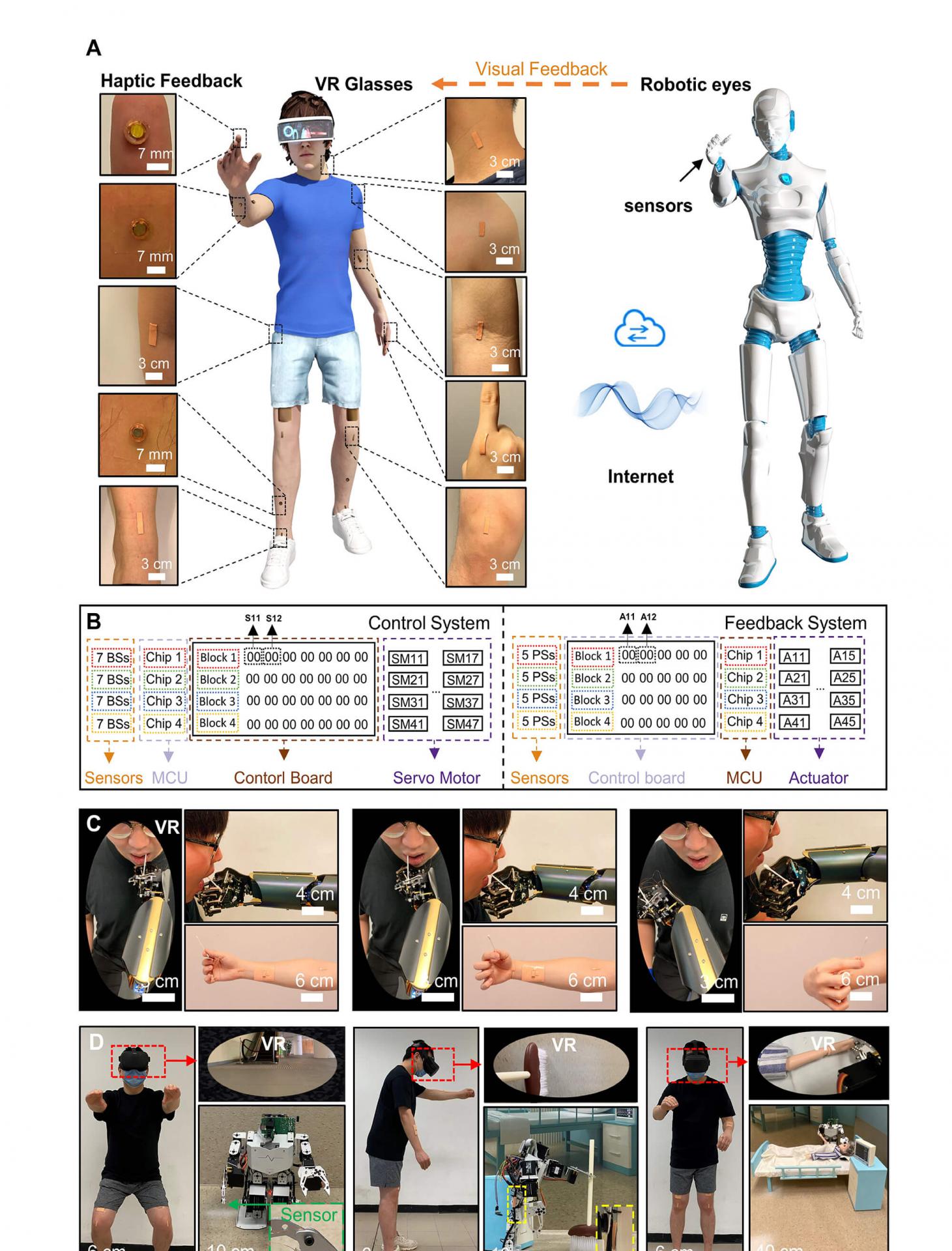 Human-Machine Interaction Device
Human-Machine Interaction Device -
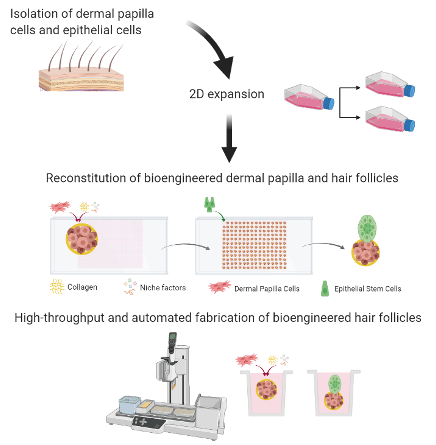 Bioengineered Hair Follicles
Bioengineered Hair Follicles -
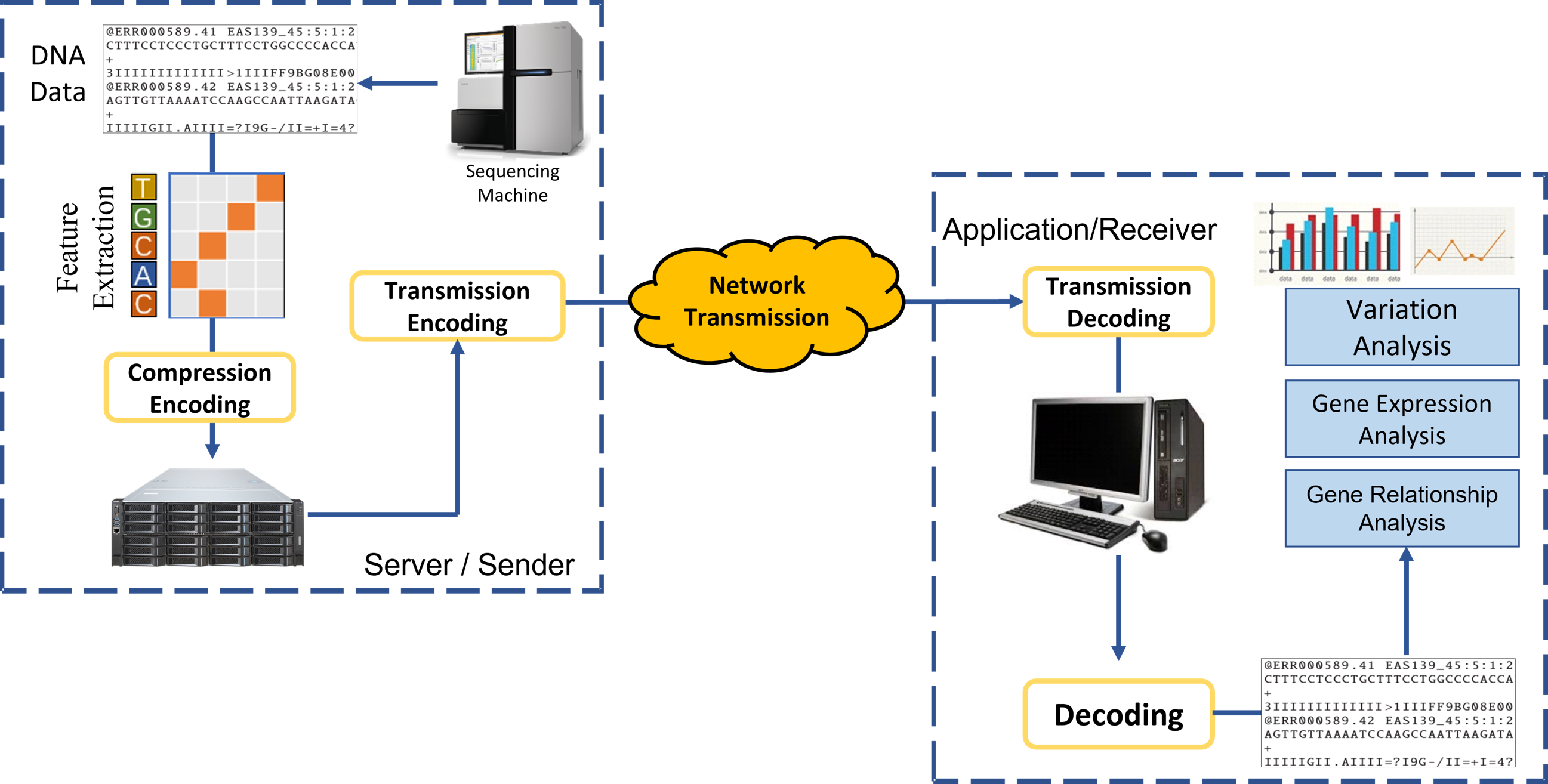 Learning-based Genome Codec
Learning-based Genome Codec -
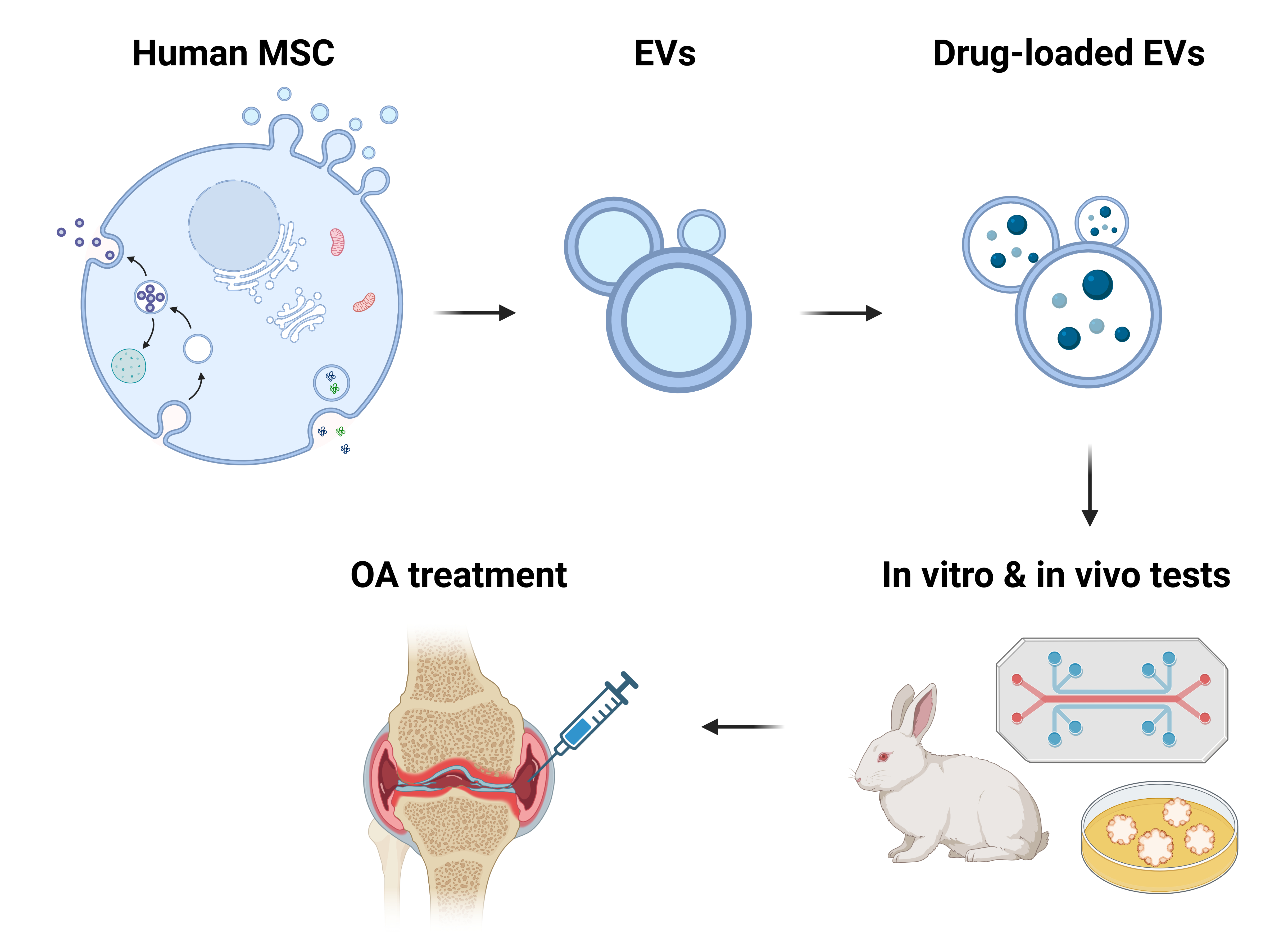 MSC-derived Extracellular Vesicles for Delivery of Osteoarthritis Drugs
MSC-derived Extracellular Vesicles for Delivery of Osteoarthritis Drugs -
 Phytonutrient-based Remedial Fluid for the Management of Hypertrophic and Keloid Scars
Phytonutrient-based Remedial Fluid for the Management of Hypertrophic and Keloid Scars -
 Anti-Cancer Combination Drug Derived from Chinese Herbs
Anti-Cancer Combination Drug Derived from Chinese Herbs -
 Novel Platform of Human Respiratory Tract
Novel Platform of Human Respiratory Tract -
 Long-lasting Spexin Could Spell the End of Obesity
Long-lasting Spexin Could Spell the End of Obesity -
 Safesugery AI system
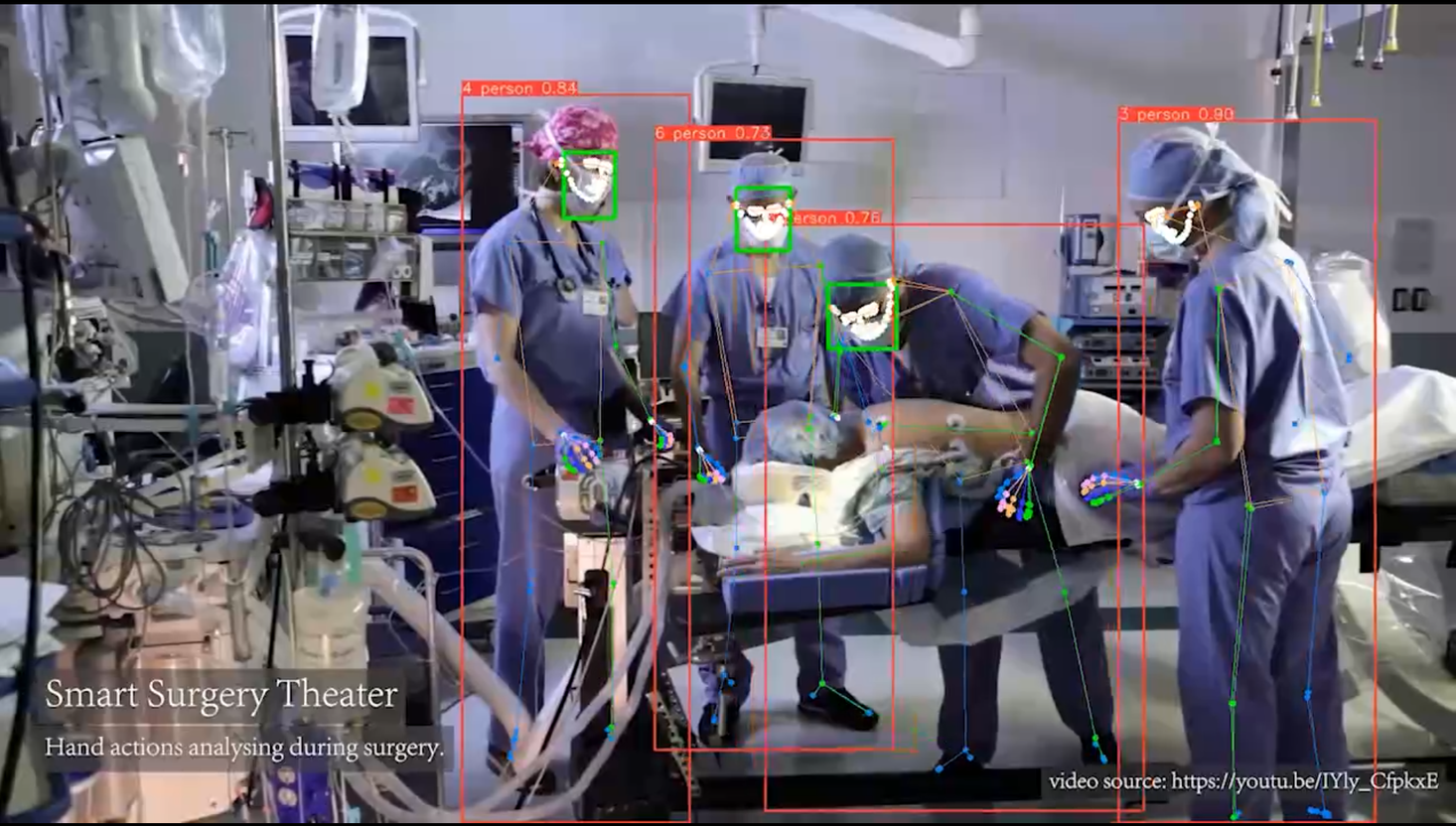
Safesugery AI system -
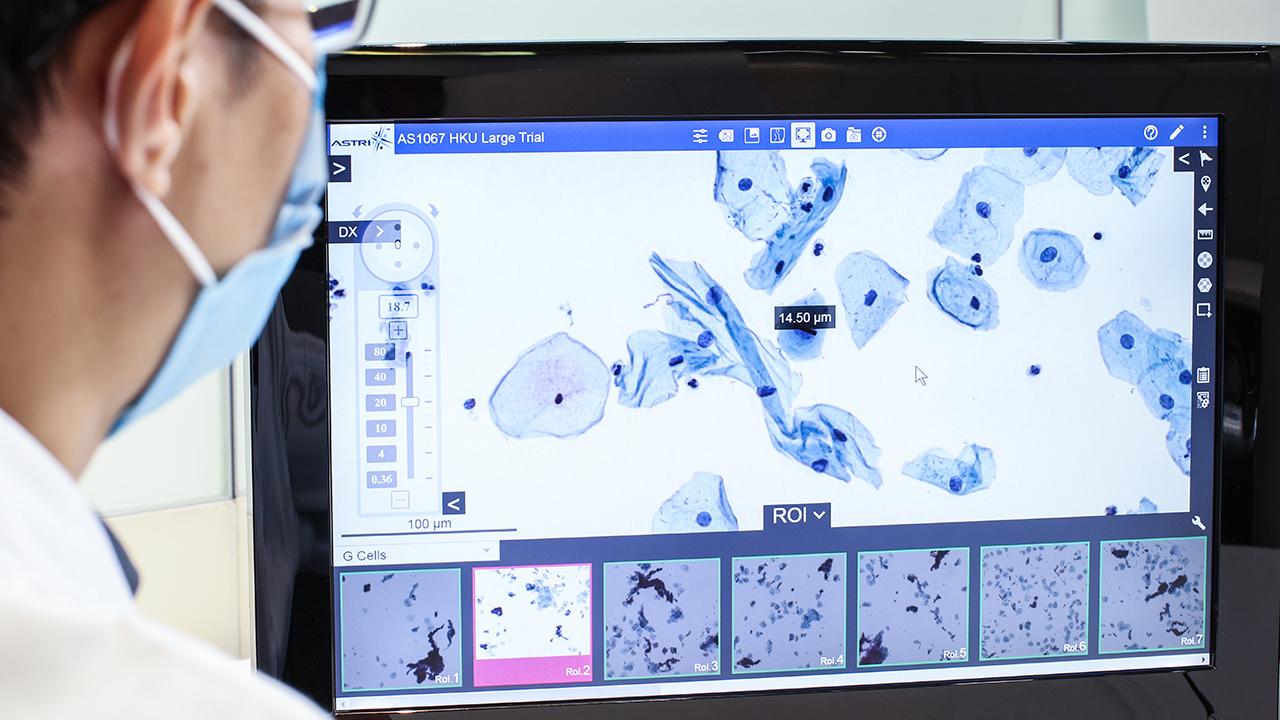
 Automated Urine Cytopathology Reporting System
Automated Urine Cytopathology Reporting System -
 Label-free High-throughput Multi-physical Cell Cytometer
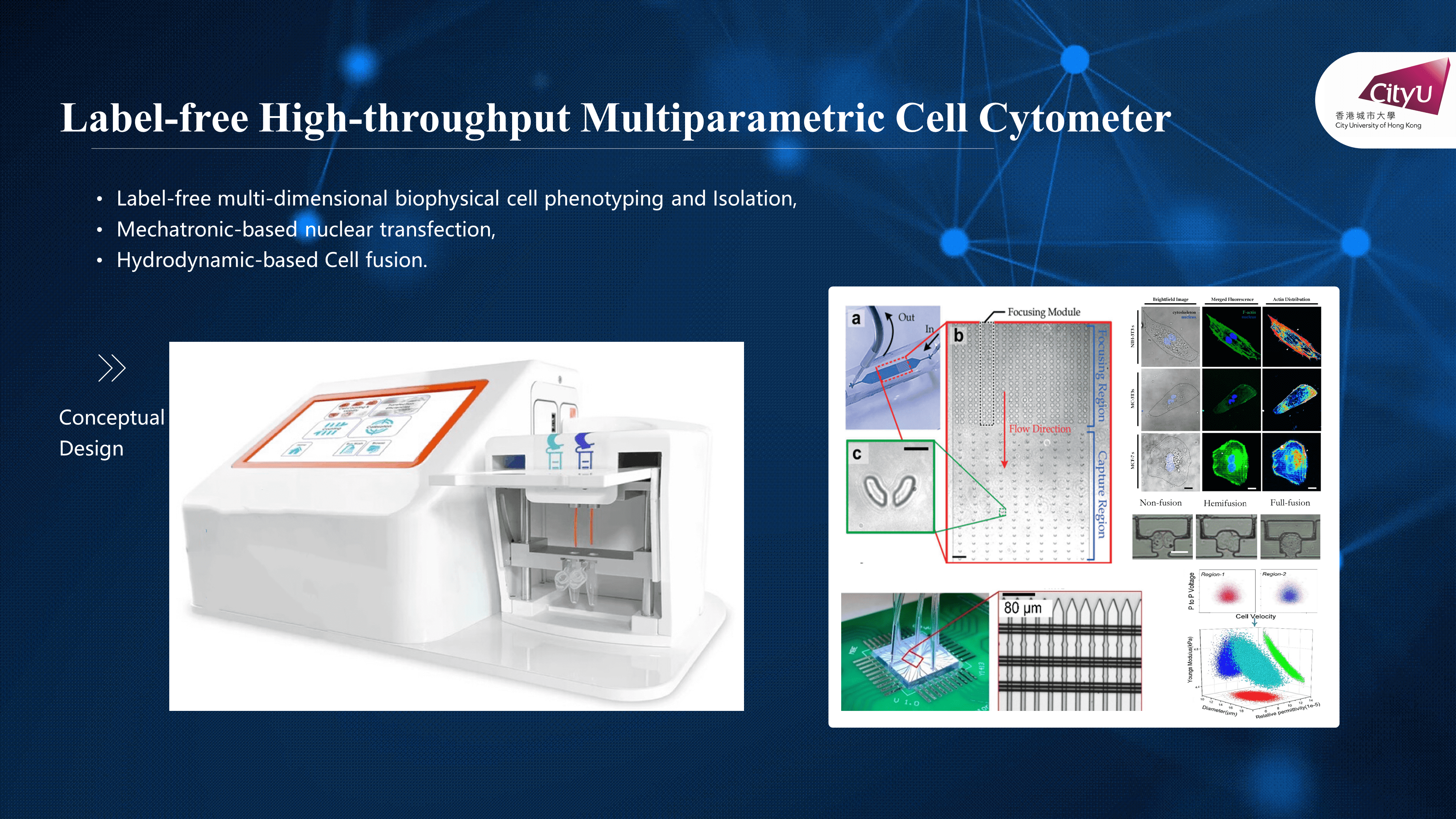
Label-free High-throughput Multi-physical Cell Cytometer -
 Biodegradable Magnesium-based Hybrid Implant
Biodegradable Magnesium-based Hybrid Implant -
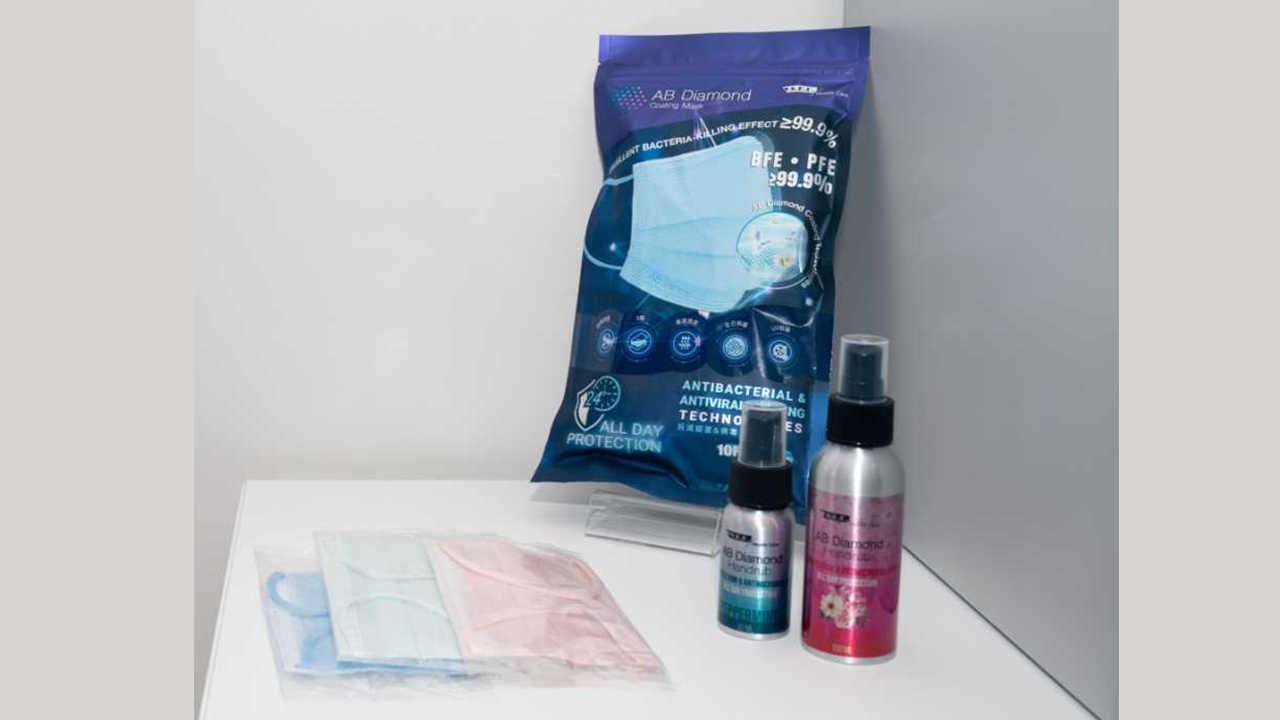 Antiviral Formulation for Personal Protective Equipment and Hand Sanitizer
Antiviral Formulation for Personal Protective Equipment and Hand Sanitizer -
 RefluxChip – A Miniature Battery-free Remote Sensing System for Real-Time Monitoring of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
RefluxChip – A Miniature Battery-free Remote Sensing System for Real-Time Monitoring of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease -
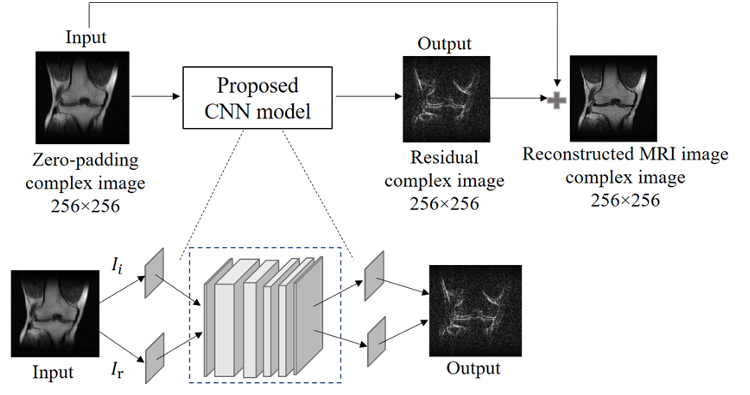 Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction from Incomplete K-Space Data
Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction from Incomplete K-Space Data -
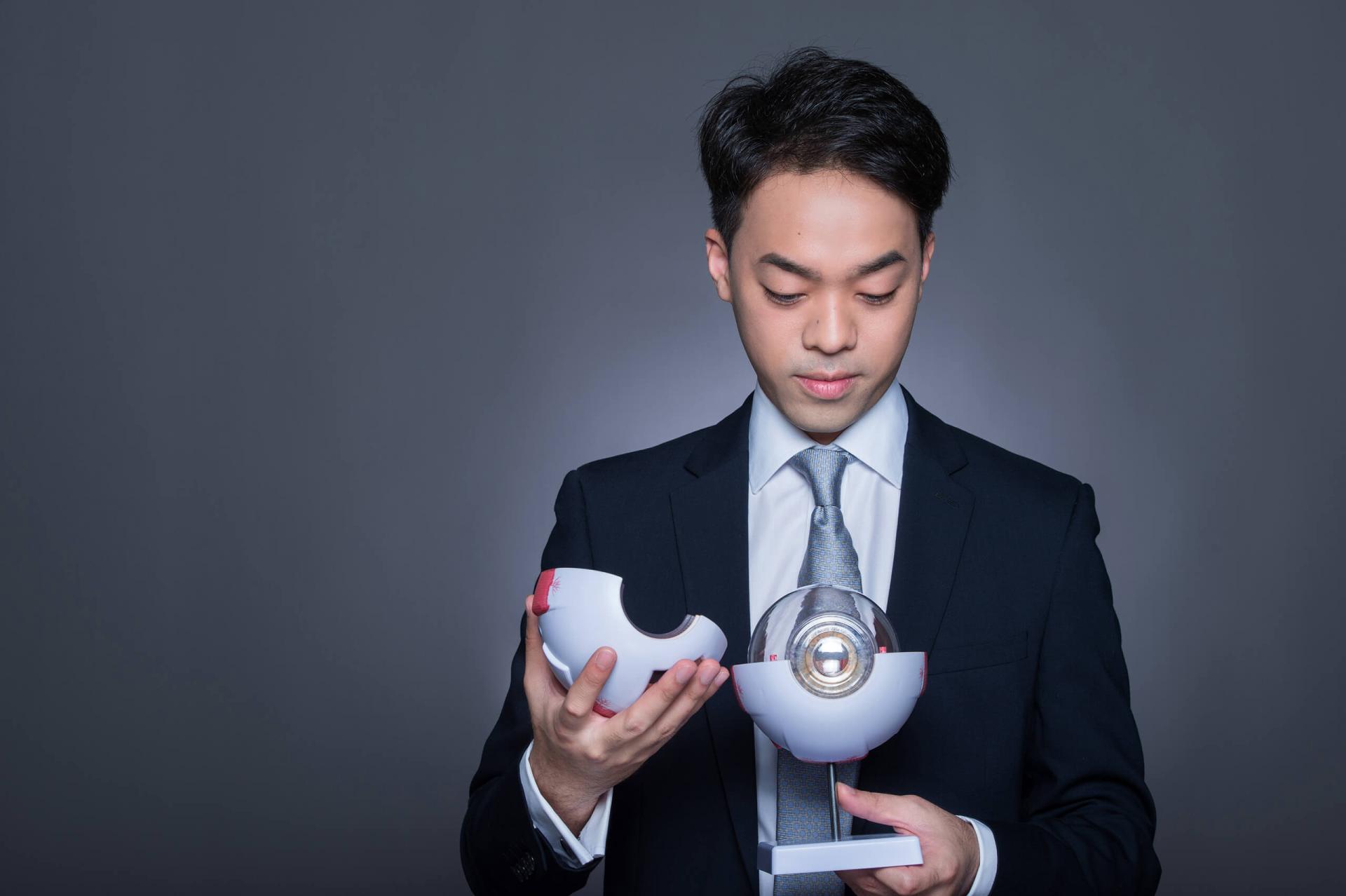 Ultrasound for Drug Delivery in Eye Care
Ultrasound for Drug Delivery in Eye Care -
 High Performance Robotic Systems for Intraoperative MRI-guided Interventions
High Performance Robotic Systems for Intraoperative MRI-guided Interventions -
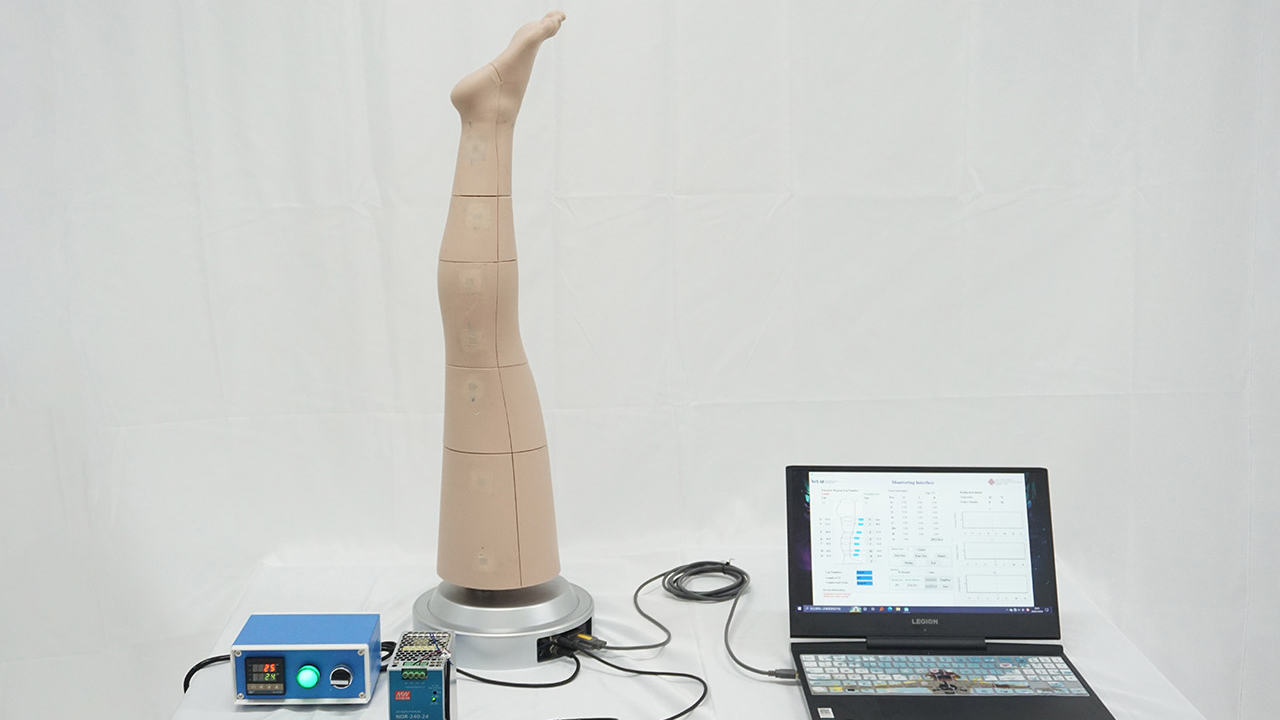 High Precision Intelligent Customisation System for Medical Pressure Garments
High Precision Intelligent Customisation System for Medical Pressure Garments -
 Diterpenoid derivatives as anticancer agents
Diterpenoid derivatives as anticancer agents -
 Natural product, Dihydro-resveratrol for treating colorectal cancer and melanoma
Natural product, Dihydro-resveratrol for treating colorectal cancer and melanoma